Rspo2 inhibits TCF3 phosphorylation to antagonize Wnt signaling during vertebrate anteroposterior axis specification
- PMID: 34183732
- PMCID: PMC8239024
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-92824-6
Rspo2 inhibits TCF3 phosphorylation to antagonize Wnt signaling during vertebrate anteroposterior axis specification
Abstract
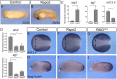
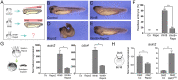
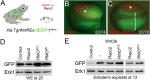
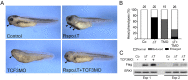
The Wnt pathway activates target genes by controlling the β-catenin-T-cell factor (TCF) transcriptional complex during embryonic development and cancer. This pathway can be potentiated by R-spondins, a family of proteins that bind RNF43/ZNRF3 E3 ubiquitin ligases and LGR4/5 receptors to prevent Frizzled degradation. Here we demonstrate that, during Xenopus anteroposterior axis specification, Rspo2 functions as a Wnt antagonist, both morphologically and at the level of gene targets and pathway mediators. Unexpectedly, the binding to RNF43/ZNRF3 and LGR4/5 was not required for the Wnt inhibitory activity. Moreover, Rspo2 did not influence Dishevelled phosphorylation in response to Wnt ligands, suggesting that Frizzled activity is not affected. Further analysis indicated that the Wnt antagonism is due to the inhibitory effect of Rspo2 on TCF3/TCF7L1 phosphorylation that normally leads to target gene activation. Consistent with this mechanism, Rspo2 anteriorizing activity has been rescued in TCF3-depleted embryos. These observations suggest that Rspo2 is a context-specific regulator of TCF3 phosphorylation and Wnt signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

