Atypical perineuronal nets in the CA2 region interfere with social memory in a mouse model of social dysfunction
- PMID: 34183768
- PMCID: PMC8712624
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-021-01174-2
Atypical perineuronal nets in the CA2 region interfere with social memory in a mouse model of social dysfunction
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Atypical perineuronal nets in the CA2 region interfere with social memory in a mouse model of social dysfunction.Mol Psychiatry. 2022 Aug;27(8):3532. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01547-1. Mol Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35459902 No abstract available.
Abstract
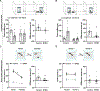
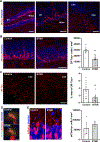
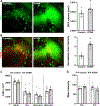
Social memory dysfunction is an especially devastating symptom of many neuropsychiatric disorders, which makes understanding the cellular and molecular processes that contribute to such abnormalities important. Evidence suggests that the hippocampus, particularly the CA2 region, plays an important role in social memory. We sought to identify potential mechanisms of social memory dysfunction in the hippocampus by investigating features of neurons, glia, and the extracellular matrix (ECM) of BTBR mice, an inbred mouse strain with deficient social memory. The CA2 is known to receive inputs from dentate gyrus adult-born granule cells (abGCs), neurons known to participate in social memory, so we examined this cell population and found fewer abGCs, as well as fewer axons from abGCs in the CA2 of BTBR mice compared to controls. We also found that BTBR mice had fewer pyramidal cell dendritic spines, in addition to fewer microglia and astrocytes, in the CA2 compared to controls. Along with diminished neuronal and glial elements, we found atypical perineuronal nets (PNNs), specialized ECM structures that regulate plasticity, in the CA2 of BTBR mice. By diminishing PNNs in the CA2 of BTBR mice to control levels, we observed a partial restoration of social memory. Our findings suggest that the CA2 region of BTBR mice exhibits multiple cellular and extracellular abnormalities and identify atypical PNNs as one mechanism producing social memory dysfunction, although the contribution of reduced abGC afferents, pyramidal cell dendritic spine, and glial cell numbers remains unexplored.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
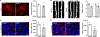
Similar articles
-
Perineuronal Nets on CA2 Pyramidal Cells and Parvalbumin-Expressing Cells Differentially Regulate Hippocampal-Dependent Memory.J Neurosci. 2025 Feb 5;45(6):e1626242024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1626-24.2024. J Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39740999 Free PMC article.
-
Perineuronal Nets Suppress Plasticity of Excitatory Synapses on CA2 Pyramidal Neurons.J Neurosci. 2016 Jun 8;36(23):6312-20. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0245-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27277807 Free PMC article.
-
Perineuronal Nets in the Dorsomedial Striatum Contribute to Behavioral Dysfunction in Mouse Models of Excessive Repetitive Behavior.Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2021 Nov 17;2(4):460-469. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsgos.2021.11.005. eCollection 2022 Oct. Biol Psychiatry Glob Open Sci. 2021. PMID: 36324654 Free PMC article.
-
Neuron-Glia Interactions in Neural Plasticity: Contributions of Neural Extracellular Matrix and Perineuronal Nets.Neural Plast. 2016;2016:5214961. doi: 10.1155/2016/5214961. Epub 2016 Jan 5. Neural Plast. 2016. PMID: 26881114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perineuronal Nets and Their Role in Synaptic Homeostasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 22;20(17):4108. doi: 10.3390/ijms20174108. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31443560 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reduced Cholecystokinin-Expressing Interneuron Input Contributes to Disinhibition of the Hippocampal CA2 Region in a Mouse Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.J Neurosci. 2023 Oct 11;43(41):6930-6949. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2091-22.2023. Epub 2023 Aug 29. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37643861 Free PMC article.
-
Social and nonsocial environmental loss have differential effects on ventral hippocampus-dependent behavior and inhibitory synaptic markers in adult male mice.Learn Mem. 2024 Dec 16;31(12):a053968. doi: 10.1101/lm.053968.124. Print 2024 Dec. Learn Mem. 2024. PMID: 39681456
-
Perineuronal nets on CA2 pyramidal cells and parvalbumin-expressing cells differentially regulate hippocampal dependent memory.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 8:2024.11.07.622463. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.07.622463. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Neurosci. 2025 Feb 05;45(6):e1626242024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1626-24.2024. PMID: 39574580 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Identification of hippocampal area CA2 in hamster and vole brain.J Comp Neurol. 2024 Mar;532(3):e25603. doi: 10.1002/cne.25603. J Comp Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38497661 Free PMC article.
-
How Stress Influences the Dynamic Plasticity of the Brain's Extracellular Matrix.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Jan 25;15:814287. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.814287. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35145379 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Williams DL, Goldstein G, Minshew NJ Impaired memory for faces and social scenes in autism: clinical implications of memory dysfunction. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 2005; 20:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Porcelli S et al. Social brain, social dysfunction and social withdrawal. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2019; 97:10–33. - PubMed
-
- García-Casal JA, Goñi-Imizcoz M, Perea-Bartolomé MV, Soto-Pérez F, Smith SJ, Calvo-Simal S, Franco-Martín M. The efficacy of emotion recognition rehabilitation for people with Alzheimer’s Disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;57:937–951. - PubMed
-
- Kogan JH, Frankland PW, Silva AJ. Long-term memory underlying hippocampus-dependent social recognition in mice. Hippocampus. 2000; 10:47–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

