DNAJA1 promotes cancer metastasis through interaction with mutant p53
- PMID: 34183772
- PMCID: PMC8804903
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-021-01921-3
DNAJA1 promotes cancer metastasis through interaction with mutant p53
Abstract
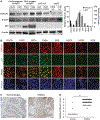
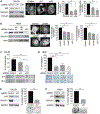
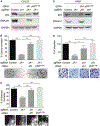
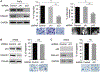
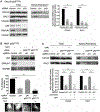
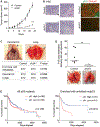
Accumulation of mutant p53 (mutp53) is crucial for its oncogenic gain of function activity. DNAJA1, a member of J-domain containing proteins or heat shock protein 40, is shown to prevent unfolded mutp53 from proteasomal degradation. However, the biological function of DNAJA1 remains largely unknown. Here we show that DNAJA1 promotes tumor metastasis by accumulating unfolded mutp53. Levels of DNAJA1 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) tissues were higher than those in normal tissues. Knockdown of DNAJA1 in HNSCC cell lines carrying unfolded mutp53 significantly decreased the levels of mutp53, filopodia/lamellipodia formation, migratory potential, and active forms of CDC42/RAC1, which were not observed in HNSCC cells with DNA contact mutp53, wild-type p53, or p53 null. Such mutp53-dependent functions of DNAJA1 were supported by the observation that DNAJA1 selectively bound to unfolded mutp53. Moreover, DNAJA1 knockdown in HNSCC cells carrying unfolded mutp53 inhibited primary tumor growth and metastases to the lymph nodes and lungs. Our study suggests that DNAJA1 promotes HNSCC metastasis mainly in a manner dependent on mutp53 status, suggesting DNAJA1 as a potential therapeutic target for HNSCC harboring unfolded mutp53.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Figures

References
-
- Cyr DM, Ramos CH. Specification of Hsp70 function by type I and type II Hsp40. Subcell Biochem. 2015;78:91–102. - PubMed
-
- Hartl FU, Bracher A, Hayer-Hartl M. Molecular chaperones in protein folding and proteostasis. Nature. 2011;475:324–32. - PubMed
-
- Large AT, Goldberg MD, Lund PA. Chaperones and protein folding in the archaea. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009;37:46–51. - PubMed
-
- Chen CY, Jan CI, Lo JF, Yang SC, Chang YL, Pan SH, et al. Tid1-L inhibits EGFR signaling in lung adenocarcinoma by enhancing EGFR Ubiquitinylation and degradation. Cancer Res. 2013;73:4009–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

