The association of transcription factor Prox1 with the proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung cancer
- PMID: 34183992
- PMCID: PMC8218550
- DOI: 10.1515/biol-2021-0056
The association of transcription factor Prox1 with the proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung cancer
Abstract
Background: The current study investigates the effect of transcription factor Prox1 on the proliferation, migration, and invasion ability of lung cancer.
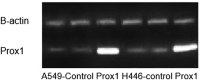
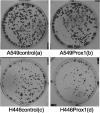
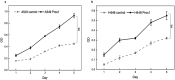
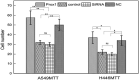
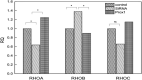
Methods: Lung cancer cell lines (A549 and H446 cells) were transfected with Prox1NAD and siRNA, respectively. Thus, the A549 and H446 cells overexpressed Prox1 after transfection of Prox1NAD plasmids, and A549 and H446 cells have low expression of Prox1 after transfection with siRNA. Reverse transcriptase quantitative PCR and western blot analyses were used to detect Prox1 mRNA and protein expression in cells. Plate clone formation experiments and MTT experiments were used to detect cell proliferation. Western blot was used to detect the expression of Rho family-related proteins in cells.
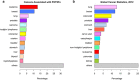
Results: Compared to untransfected wild-type A549 and H446 that served as blank controls, the expression level of Prox1mRNA and protein in A549 and H446 cells overexpressing Prox1 after plasmid transfection was high, while the expression level of Prox1mRNA and protein in A549 and H446 cells with low expression of Prox1 after siRNA transfection was low. With the increase of Prox1 expression, the expression of RhoA and RhoC increased, while the expression of RhoB decreased.
Conclusion: The finding of this study may provide a new approach for the treatment of lung cancer using targeted gene therapy.
Keywords: Rho family; invasion; lung cancer; migration; transcription factor Prox1.
© 2021 Xinxin Hao et al., published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Agnihotri NS, Astekar M. The role of novel prognostic markers PROX1 and FOXC2 in carcinogenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Exp Ther Oncol. 2018;12(3):171–84. - PubMed
- Agnihotri NS, Astekar M. The role of novel prognostic markers PROX1 and FOXC2 in carcinogenesis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Exp Ther Oncol. 2018;12(3):171–84. - PubMed
-
- Zeng H, Zheng R, Guo Y, Zhang S, Zou X, Wang N, et al. Cancer survival in China, 2003–2005: a population-based study. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(8):1921–30. - PubMed
- Zeng H, Zheng R, Guo Y, Zhang S, Zou X, Wang N. et al. Cancer survival in China, 2003–2005: a population-based study. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(8):1921–30. - PubMed
-
- Gao T, Ma C, Li Y, Ju J, Kang X, Cai Y, et al. High expression of prospero-related homeobox-1 (Prox1) is associated with poor prognosis in patients with salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;76(7):1440–6. - PubMed
- Gao T, Ma C, Li Y, Ju J, Kang X, Cai Y. et al. High expression of prospero-related homeobox-1 (Prox1) is associated with poor prognosis in patients with salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;76(7):1440–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
