Effect of melatonin supplementation on endothelial function in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: A randomized, double-blinded clinical trial
- PMID: 34184295
- PMCID: PMC8427988
- DOI: 10.1002/clc.23682
Effect of melatonin supplementation on endothelial function in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: A randomized, double-blinded clinical trial
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to investigate the effect of melatonin supplementation on endothelial function in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF).
Methods: This is an analysis of the MeHR trial, a randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled clinical trial with two parallel arms of 1:1. Oral 10 mg melatonin tablets or placebo was administered for 24 weeks. Deference in the percentage of flow-mediated dilatation (FMD) after the intervention was the primary outcome.
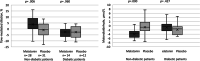
Results: Ninety-two patients were included in the study (age: 62.7±10.3 years, 87.0% male, ejection fraction (EF): 28.6±8.1). After adjustment for baseline FMD and age, a statistically significant difference in post-treatment FMD in favor of the melatonin group was seen (estimated marginal means [95%CI], melatonin: 7.84% [6.69-8.98], placebo: 5.98% [4.84-7.12], p = .027). There was no significant difference in the mean of post-treatment systolic/diastolic blood pressure, serum total antioxidant capacity, and serum malondialdehyde (MDA) between groups. Subgroup analysis showed significant improvement in FMD and MDA in the melatonin group in nondiabetic patients, while no difference was seen between study groups in diabetic patients.
Conclusions: Melatonin supplementation in HFrEF might improve endothelial function; however, this beneficial effect might not be seen in diabetic patients.
Keywords: blood pressure; endothelial dysfunction; heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; melatonin; oxidative stress.
© 2021 The Authors. Clinical Cardiology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zuchi C, Tritto I, Carluccio E, Mattei C, Cattadori G, Ambrosio G. Role of endothelial dysfunction in heart failure. Heart Fail Rev. 2020;25(1):21‐30. - PubMed
-
- Canetti M, Akhter MW, Lerman A, et al. Evaluation of myocardial blood flow reserve in patients with chronic congestive heart failure due to idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Am J Card. 2003;92(10):1246‐1249. - PubMed
-
- Areas GPT, Mazzuco A, Caruso FR, et al. Flow‐mediated dilation and heart failure: a review with implications to physical rehabilitation. Heart Fail Rev. 2019;24(1):69‐80. - PubMed
-
- Galano A, Reiter RJ. Melatonin and its metabolites vs oxidative stress: from individual actions to collective protection. J Pineal Res. 2018;65(1):e12514. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

