Bevacizumab biosimilar LY01008 compared with bevacizumab (Avastin) as first-line treatment for Chinese patients with unresectable, metastatic, or recurrent non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer: A multicenter, randomized, double-blinded, phase III trial
- PMID: 34184418
- PMCID: PMC8441057
- DOI: 10.1002/cac2.12179
Bevacizumab biosimilar LY01008 compared with bevacizumab (Avastin) as first-line treatment for Chinese patients with unresectable, metastatic, or recurrent non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer: A multicenter, randomized, double-blinded, phase III trial
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have demonstrated the preclinical pharmacological and toxicological consistency, and clinical pharmacokinetic equivalence of bevacizumab biosimilar LY01008 with reference bevacizumab (Avastin). This randomized controlled trial aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of LY01008 with Avastin in first-line treatment of Chinese patients with advanced or recurrent non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
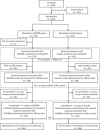
Methods: Stage IIIB-IV NSCLC patients with evaluable lesions, good physical status, and adequate organ functions from 67 centers across China were randomized in a ratio of 1:1 to receive LY01008 or Avastin 15 mg/kg intravenously in combination with paclitaxel/carboplatin (combined treatment) for 4-6 cycles, followed by maintenance monotherapy with LY01008 until disease progression, intolerable toxicity, or death. The primary endpoint was objective response rate (ORR) in accordance with Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) version 1.1 confirmed by independent radiological review committees (IRRC). Secondary endpoints included disease control rate (DCR), duration of response (DoR), progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and safety. This study was registered in ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT03533127).
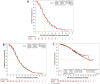
Results: Between December 15th , 2017, and May 15th , 2019, a total of 649 patients were randomized to the LY01008 (n = 324) or Avastin (n = 325) group. As of September 25th , 2019 for primary endpoint analysis, 589 patients received ORR evaluation, with a median number of combined treatment cycles of 5 (range 1-6) and median duration of treatment of 3.0 (range 0.0-5.1) months. ORR of response-evaluable patients in the LY01008 and Avastin groups were 48.5% and 53.0%, respectively. The stratified ORR ratio was 0.91 (90% CI 0.80-1.04, within the prespecified equivalence margin of 0.75-1.33). Up to May 15th , 2020, with a median follow-up of 13.6 (range 0.8-28.4) months, no notable differences in DCR, median DoR, median PFS, median OS, and 1-year OS rate were observed between the LY01008 and Avastin groups. There were no clinically meaningful differences in safety and immunogenicity across treatment groups.
Conclusions: LY01008 demonstrated similarity to Avastin in terms of efficacy and safety in Chinese patients with advanced or recurrent non-squamous NSCLC. LY01008 combined with paclitaxel/carboplatin is expected to become a new treatment option for unresectable, metastatic, or recurrent non-squamous NSCLC patients in the first-line setting.
Keywords: LY01008; anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody; anti-angiogenesis; avastin; bevacizumab; biosimilar; non-small cell lung cancer; vascular endothelial growth factor.
© 2021 The Authors. Cancer Communications published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd. on behalf of Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center.
Conflict of interest statement
The tested drug LY01008 in this study is the product of Luye Pharma Group Ltd., which provided main funding to this study. Emei Gao, Li Zhao, Shumin Wang, and Can Wu are employees of the Clinical Research Center of Luye Pharma Group Ltd., Luye Life Sciences Group, Beijing, China. All other authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(2):115–32. - PubMed
-
- Reck M, Heigener DF, Mok T, Soria JC, Rabe KF. Management of non‐small‐cell lung cancer: recent developments. Lancet. 2013;382(9893):709–19. - PubMed
-
- Yang P, Allen MS, Aubry MC, Wampfler JA, Marks RS, Edell ES, et al. Clinical features of 5,628 primary lung cancer patients: experience at Mayo Clinic from 1997 to 2003. Chest. 2005;128(1):452–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

