Fimasartan-Based Blood Pressure Control after Acute Cerebral Ischemia: The Fimasartan-Based Blood Pressure Control after Acute Cerebral Ischemia Study
- PMID: 34184441
- PMCID: PMC8242309
- DOI: 10.3988/jcn.2021.17.3.344
Fimasartan-Based Blood Pressure Control after Acute Cerebral Ischemia: The Fimasartan-Based Blood Pressure Control after Acute Cerebral Ischemia Study
Abstract
Background and purpose: Blood pressure (BP) control is strongly recommended, but BP control rate has not been well studied in patients with stroke. We evaluated the BP control rate with fimasartan-based antihypertensive therapy initiated in patients with recent cerebral ischemia.
Methods: This multicenter, prospective, single-arm trial involved 27 centers in South Korea. Key inclusion criteria were recent cerebral ischemia within 90 days and high BP [systolic blood pressure (SBP) >140 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) >90 mm Hg]. BP lowering was initiated with fimasartan. BP management during the follow-up was at the discretion of the responsible investigators. The primary endpoint was the target BP goal achievement rate (<140/90 mm Hg) at 24 weeks. Key secondary endpoints included achieved BP and BP changes at each visit, and clinical events (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03231293).
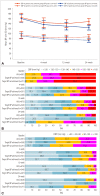
Results: Of 1,035 patients enrolled, 1,026 were included in the safety analysis, and 951 in the efficacy analysis. Their mean age was 64.1 years, 33% were female, the median time interval from onset to enrollment was 10 days, and the baseline SBP and DBP were 162.3±16.0 and 92.2±12.4 mm Hg (mean±SD). During the study period, 55.5% of patients were maintained on fimasartan monotherapy, and 44.5% received antihypertensive therapies other than fimasartan monotherapy at at least one visit. The target BP goal achievement rate at 24-week was 67.3% (48.6% at 4-week and 61.4% at 12-week). The mean BP was 139.0/81.8±18.3/11.7, 133.8/79.2±16.4/11.0, and 132.8/78.5±15.6/10.9 mm Hg at 4-, 12-, and 24-week. The treatment-emergent adverse event rate was 5.4%, including one serious adverse event.
Conclusions: Fimasartan-based BP lowering achieved the target BP in two-thirds of patients at 24 weeks, and was generally well tolerated.
Keywords: blood pressure; fimasartan; prevention and control; stroke.
Copyright © 2021 Korean Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
All the investigators received research grant based on the study contracts for the number of subjects enrolled and/or for the conduct of the study from Boryung Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Seoul, Korea.
Figures
References
-
- Grau AJ, Weimar C, Buggle F, Heinrich A, Goertler M, Neumaier S, et al. Risk factors, outcome, and treatment in subtypes of ischemic stroke: the German stroke data bank. Stroke. 2001;32:2559–2566. - PubMed
-
- Kimura K, Kazui S, Minematsu K, Yamaguchi T. Analysis of 16,922 patients with acute ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack in Japan. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2004;18:47–56. - PubMed
-
- Fonarow GC, Reeves MJ, Smith EE, Saver JL, Zhao X, Olson DW, et al. Characteristics, performance measures, and in-hospital outcomes of the first one million stroke and transient ischemic attack admissions in get with the guidelines-stroke. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2010;3:291–302. - PubMed
-
- PROGRESS Collaborative Group. Randomised trial of a perindoprilbased blood-pressure-lowering regimen among 6,105 individuals with previous stroke or transient ischaemic attack. Lancet. 2001;358:1033–1041. - PubMed
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

