Legionella pneumophila LegC7 effector protein drives aberrant endoplasmic reticulum:endosome contacts in yeast
- PMID: 34184807
- PMCID: PMC8319159
- DOI: 10.1111/tra.12807
Legionella pneumophila LegC7 effector protein drives aberrant endoplasmic reticulum:endosome contacts in yeast
Abstract
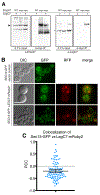
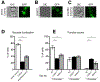
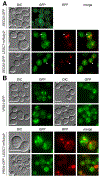
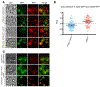
Legionella pneumophila is a facultative intracellular bacterial pathogen, causing the severe form of pneumonia known as Legionnaires' disease. Legionella actively alters host organelle trafficking through the activities of "effector" proteins secreted via a type-IVB secretion system, in order to construct the bacteria-laden Legionella-containing vacuole (LCV) and prevent lysosomal degradation. The LCV is created with membrane derived from host endoplasmic reticulum (ER), secretory vesicles and phagosomes, although the precise molecular mechanisms that drive its synthesis remain poorly understood. In an effort to characterize the in vivo activity of the LegC7/YlfA SNARE-like effector protein from Legionella in the context of eukaryotic membrane trafficking in yeast, we find that LegC7 interacts with the Emp46p/Emp47p ER-to-Golgi glycoprotein cargo adapter complex, alters ER morphology and induces aberrant ER:endosome interactions, as measured by visualization of ER cargo degradation, reconstitution of split-GFP proteins and enhanced oxidation of the ER lumen. LegC7-dependent toxicity, disruption of ER morphology and ER:endosome fusion events were dependent upon endosomal VPS class C tethering complexes and the endosomal t-SNARE, Pep12p. This work establishes a model in which LegC7 functions to recruit host ER material to the bacterial phagosome during infection by driving ER:endosome contacts, potentially through interaction with host membrane tethering complexes and/or cargo adapters.
Keywords: LegC7; Legionella pneumophila; SNARE proteins; Saccharomyces cerevisiae; VPS class C tethering complexes; cargo adapters; membrane fusion.
© 2021 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures





References
-
- Dooling KL, et al. , Active Bacterial Core Surveillance for Legionellosis - United States, 2011-2013. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep, 2015. 64(42): p. 1190–3. - PubMed
-
- Prevention, C.f.D.C.a., National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System, 2017 Annual Tables of Infectious Disease Data. 2018, CDC Division of Health Informatics and Surveillance, 2018: Atlanta, GA.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

