How molecular imaging will enable robotic precision surgery : The role of artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and navigation
- PMID: 34185136
- PMCID: PMC8566413
- DOI: 10.1007/s00259-021-05445-6
How molecular imaging will enable robotic precision surgery : The role of artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and navigation
Abstract
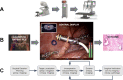
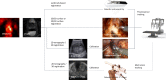
Molecular imaging is one of the pillars of precision surgery. Its applications range from early diagnostics to therapy planning, execution, and the accurate assessment of outcomes. In particular, molecular imaging solutions are in high demand in minimally invasive surgical strategies, such as the substantially increasing field of robotic surgery. This review aims at connecting the molecular imaging and nuclear medicine community to the rapidly expanding armory of surgical medical devices. Such devices entail technologies ranging from artificial intelligence and computer-aided visualization technologies (software) to innovative molecular imaging modalities and surgical navigation (hardware). We discuss technologies based on their role at different steps of the surgical workflow, i.e., from surgical decision and planning, over to target localization and excision guidance, all the way to (back table) surgical verification. This provides a glimpse of how innovations from the technology fields can realize an exciting future for the molecular imaging and surgery communities.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Augmented reality; Image-guided surgery; Molecular imaging; Precision surgery; Robotic surgery.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
TW is a consultant for technology developments for the medical device companies SurgicEye and Crystal Photonics. FvL is a consultant for the medical device company Hamamatsu Photonics. The remaining authors do not have any conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures





References
-
- Lidsky ME, D’Angelica MI. An outlook on precision surgery. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2017;43(5):853–855. - PubMed
-
- Harbin AC, Eun DD. The role of extended pelvic lymphadenectomy with radical prostatectomy for high-risk prostate cancer. Urol Oncol. 2015;33(5):208–216. - PubMed
-
- Tsai S-H, Tseng P-T, Sherer BA, Lai Y-C, Lin P-Y, Wu C-K, Stoller ML. Open versus robotic partial nephrectomy: Systematic review and meta-analysis of contemporary studies. Int J Med Robot. 2019;15(1):e1963. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

