Impact of financial medication assistance on medication adherence: a systematic review
- PMID: 34185554
- PMCID: PMC10084847
- DOI: 10.18553/jmcp.2021.27.7.924
Impact of financial medication assistance on medication adherence: a systematic review
Abstract
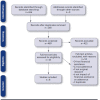
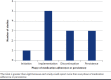
BACKGROUND: The prevalence of financial medication assistance (FMA), including patient assistance programs, coupons/copayment cards, vouchers, discount cards, and programs/pharmacy services that help patients apply for such programs, has increased. The impact of FMA on medication adherence and persistence has not been synthesized. OBJECTIVE: The primary objective of this study was to review published studies evaluating the impact of FMA on the three phases of medication adherence (initiation [or primary adherence], implementation [or secondary adherence], and discontinuation) and persistence. Among these studies, the secondary objective was to report the impact of FMA on patient out-of-pocket costs and clinical outcomes. METHODS: A systematic review was performed using MEDLINE and Web of Science. RESULTS: Of 656 articles identified, eight studies met all inclusion criteria. Seven studies examined FMA for medications treating cardiovascular diseases, while one study assessed FMA for cancer medications. Among included studies, FMA had a positive impact on medication adherence or persistence, and most measured this impact over one year or less. Of the three phases of medication adherence, implementation (5 of 8) was most commonly reported, followed by discontinuation (3 of 8), and then initiation (1 of 8). Regarding implementation, users of FMA had a higher mean medication possession ratio (MPR) than nonusers, ranging from 7 to 18 percentage points higher. The percentage of patients who discontinued medication was 7 percentage points lower in users of FMA versus nonusers for cardiovascular disease states. In one cancer study, FMA had a larger impact on initiation than discontinuation, ie, compared to nonusers, users of FMA were less likely to abandon an initial prescription (risk ratio= 0.12, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.08-0.18), and this effect was larger than the decreased likelihood of discontinuing the medication (hazard ratio = 0.76, 95% CI: 0.66-0.88). In 3 of 8 studies reporting on medication persistence, FMA increased the odds of medication persistence for one year ranged from 11% to 47%, depending on the study. In addition to adherence, half of the studies reported on FMA impacts on patient out-of-pocket costs and 3 of 8 studies reported on clinical outcomes. Impacts on patient out-of-pocket costs were mixed; two studies reported that out-of-pocket costs were higher for users of a coupon or a voucher versus nonusers, one study reported the opposite, and one study reported null effects. Impacts on clinical outcomes were either positive or null. CONCLUSIONS: We found that FMA has positive impacts on all phases of medication adherence as well as medication persistence over one year. Future studies should assess whether FMA has differential impacts based on phase of medication adherence and report on its longer-term (ie, beyond one year) impacts on medication adherence. DISCLOSURES: This work was sponsored by a grant from Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA). PhRMA had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. Hung reports past employment by Blue Cross Blue Shield Association and CVS Health and a grant from PhRMA outside of the submitted work. Zullig reports research funding from Proteus Digital Health and the PhRMA Foundation. consulting fees from Novartis. Reed reports receiving research support from Abbott Vascular, AstraZeneca, Janssen Research & Development, Monteris, PhRMA Foundation, and TESARO and consulting fees from Sanofi/Regeneron, NovoNordisk, SVC Systems, and Minomic International, Inc. Bosworth reports research grants from the PhRMA Foundation, Proteus Digital Health, Otsuka, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Improved Patient Outcomes, Boehinger Ingelheim, NIH, and VA, as well as consulting fees from Sanofi, Novartis, Otsuka, Abbott, Xcenda, Preventric Diagnostics, and the Medicines Company. The other authors have nothing to report. This work was presented as a poster presentation at the ESPACOMP Annual Meeting in November 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was sponsored by a grant from Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA). PhRMA had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. Hung reports past employment by Blue Cross Blue Shield Association and CVS Health and a grant from PhRMA outside of the submitted work. Zullig reports research funding from Proteus Digital Health and the PhRMA Foundation. consulting fees from Novartis. Reed reports receiving research support from Abbott Vascular, AstraZeneca, Janssen Research & Development, Monteris, PhRMA Foundation, and TESARO and consulting fees from Sanofi/Regeneron, NovoNordisk, SVC Systems, and Minomic International, Inc. Bosworth reports research grants from the PhRMA Foundation, Proteus Digital Health, Otsuka, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Improved Patient Outcomes, Boehinger Ingelheim, NIH, and VA, as well as consulting fees from Sanofi, Novartis, Otsuka, Abbott, Xcenda, Preventric Diagnostics, and the Medicines Company. The other authors have nothing to report.
This work was presented as a poster presentation at the ESPACOMP Annual Meeting in November 2020.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sustained long-term benefits of patient support program participation in immune-mediated diseases: improved medication-taking behavior and lower risk of a hospital visit.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2021 Aug;27(8):1086-1095. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2021.20560. Epub 2021 Apr 12. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2021. PMID: 33843252 Free PMC article.
-
Patient Support Program Increased Medication Adherence with Lower Total Health Care Costs Despite Increased Drug Spending.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2019 Jul;25(7):770-779. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2019.18443. Epub 2019 May 11. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2019. PMID: 31081461 Free PMC article.
-
Objective medication adherence and persistence in people with multiple sclerosis: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2021 Sep;27(9):1273-1295. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2021.27.9.1273. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2021. PMID: 34464209 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Cost Generic Program Use by Medicare Beneficiaries: Implications for Medication Exposure Misclassification in Administrative Claims Data.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2016 Jun;22(6):741-51. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2016.22.6.741. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2016. PMID: 27231801 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Methods to Measure Oral Oncolytic Dose Intensity Using Retrospective Data.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2019 Oct;25(10):1125-1132. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2019.25.10.1125. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2019. PMID: 31556821 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pharmaco-disparities in heart failure: a survey of the affordability of guideline recommended therapy in 10 countries.ESC Heart Fail. 2023 Oct;10(5):3152-3163. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14468. Epub 2023 Aug 30. ESC Heart Fail. 2023. PMID: 37646297 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating Financial Incentives as a Tool to Increase Medication Adherence for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Diabetes Ther. 2025 Mar;16(3):527-545. doi: 10.1007/s13300-025-01694-y. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Diabetes Ther. 2025. PMID: 39928226 Free PMC article.
-
Delving into the Elements Impacting Treatment Acceptance among patients with Substance Use Disorder using Health Belief Model: a qualitative study.BMC Psychol. 2025 Feb 28;13(1):177. doi: 10.1186/s40359-025-02469-7. BMC Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40022272 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment out-of-pocket cost communication and remote financial navigation in patients with cancer: a feasibility study.Support Care Cancer. 2022 Oct;30(10):8173-8182. doi: 10.1007/s00520-022-07270-5. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Support Care Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35796885 Free PMC article.
-
A Pilot Study of Hemoglobin A1C Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes after Creation of a Patient Assistance Program Enrollment Committee at a Student-Run Free Clinic.Innov Pharm. 2025 Jan 14;15(4):10.24926/iip.v15i4.6435. doi: 10.24926/iip.v15i4.6435. eCollection 2024. Innov Pharm. 2025. PMID: 40401297 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Poll: Nearly 1 in 4 Americans Taking Prescription Drugs Say It’s Difficult to Afford Their Medicines, including Larger Shares Among Those with Health Issues, with Low Incomes and Nearing Medicare Age. KFF.org. Published March 1, 2019. Accessed September 1, 2020. https://www.kff.org/health-costs/press-release/poll-nearly-1-in-4-americ...
-
- Curkendall S, Patel V, Gleeson M, et al. . Compliance with biologic therapies for rheumatoid arthritis: do patient out-of-pocket payments matter? Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59(10):1519-26. doi:10.1002/art.24114 - PubMed
-
- St Charles M, Bollu VK, Hornyak E, et al. . Predictors of Treatment Non-Adherence in Patients Treated with Imatinib Mesylate for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Blood. 2009;114(22):2209. doi:10.1182/blood. V114.22.2209.2209 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous