Circulating furin, IL-6, and presepsin levels and disease severity in SARS-CoV-2-infected patients
- PMID: 34187224
- PMCID: PMC10305811
- DOI: 10.1177/00368504211026119
Circulating furin, IL-6, and presepsin levels and disease severity in SARS-CoV-2-infected patients
Abstract
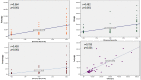
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has resulted in a vast number of infections and deaths that deeply affect the world. When the virus encounters the host cell, it binds to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, then the S protein of the virus is broken down by the transmembrane protease serine 2 with the help of furin, allowing the virus to enter the cell. The elevated inflammatory cytokines suggest that a cytokine storm, also known as cytokine release syndrome, may play a major role in the pathology of COVID-19. Therefore, the aim of this study is to investigate the relationship between circulating furin levels, disease severity, and inflammation in patients with SARS-CoV-2. A total of 52 SARS-CoV-2 patients and 36 healthy control participants were included in this study. SARS- CoV-2 patients were scored by the disease activity score. Serum furin, presepsin, and interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels were assessed using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The mean furin, presepsin, and IL-6 levels were significantly higher in the peripheral blood of SARS-CoV-2 compared to the controls (p < 0.001). There were close positive relationship between serum furin and IL-6, furin and presepsin, and furin and disease severity (r = 0.793, p < 0001; r = 0.521, p < 0.001; and r = 0,533, p < 0.001, respectively) in patients with SARS-CoV-2. These results suggest that furin may contribute to the exacerbation of SARS-CoV-2 infection and increased inflammation, and could be used as a predictor of disease severity in COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: IL-6; SARS-CoV-2; disease severity; furin; inflammation; presepsin.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous