Prognostic nomogram for hepatocellular carcinoma with radiofrequency ablation: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 34187430
- PMCID: PMC8243759
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-08505-0
Prognostic nomogram for hepatocellular carcinoma with radiofrequency ablation: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is an effective treatment option for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This study aimed to analyze the prognostic factors of HCC patients treated with RFA and to develop nomograms for outcome prediction.
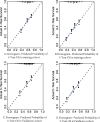
Methods: A total of 3142 HCC patients treated with RFA were recruited, and their data were collected from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database. Univariate and multifactor Cox analyses were performed to identify independent prognostic factors. These factors were integrated into a nomogram to predict 3- and 5-year cancer-specific survival (CSS) and overall survival (OS). Consistency indices and calibration plots were used to assess the accuracy of the nomograms in both the internal and external cohorts.
Results: The median follow-up periods for HCC patients treated with RFA were 27 and 29 months for OS and CSS, respectively. Marital status, age, race, histological grade of differentiation, tumor size, T stage, and serum alpha-fetoprotein levels at the time of diagnosis were identified as prognostic factors for OS and CSS. Additionally, M stage was identified as risk factors for OS. These risk factors are included in the nomogram. The calibration plots of the OS and CSS nomograms showed excellent consistency between actual survival and nomogram predictions. The bootstrap-corrected concordance indices of the OS and CSS nomograms were 0.637 (95% CI, 0.628-0.646) and 0.670 (95% 0.661-0.679), respectively. Importantly, our nomogram performed better discriminatory compared with 8th edition tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) stage system for predicting OS and CSS.
Conclusions: We identified prognostic factors for HCC patients treated with RFA and provided an accurate and personalized survival prediction scheme.
Keywords: Cancer-specific survival (CSS); Hepatocellular carcinoma; Nomogram; Overall survival (OS); Radiofrequency ablation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Nomograms to Predict the Disease-free Survival and Overall Survival after Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Intern Med. 2018 Feb 15;57(4):457-468. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9064-17. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Intern Med. 2018. PMID: 29151504 Free PMC article.
-
Retrospective Analysis of Radiofrequency Ablation in Patients with Small Solitary Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Survival Outcomes and Development of a Machine Learning Prognostic Model.Curr Med Sci. 2024 Oct;44(5):1006-1017. doi: 10.1007/s11596-024-2900-4. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Curr Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39347922
-
Predicting cancer-specific mortality in T1/2 hepatocellular carcinoma after radiofrequency ablation by competing risk nomogram: A population-based analysis.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2024 Feb;48(2):102283. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2024.102283. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38219821
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prognostic Nomograms After UTUC Surgery.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 1;12:907975. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.907975. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35847838 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and Clinical Application of the Nomogram Related to Risk or Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2023 Aug 22;10:1389-1398. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S417123. eCollection 2023. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2023. PMID: 37637500 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterizing hepatocellular carcinoma stem markers and their corresponding susceptibility to NK-cell based immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 26;14:1284669. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1284669. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37954598 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting histologic differentiation of solitary hepatocellular carcinoma up to 5 cm on gadoxetate disodium-enhanced MRI.Insights Imaging. 2023 Jan 8;14(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s13244-022-01354-w. Insights Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36617583 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a transformer model for predicting the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after radiofrequency ablation.Hepatol Int. 2024 Feb;18(1):131-137. doi: 10.1007/s12072-023-10585-y. Epub 2023 Sep 9. Hepatol Int. 2024. PMID: 37689614 Free PMC article.
-
A novel prognostic nomogram for hepatocellular carcinoma after thermal ablation.Am J Cancer Res. 2021 Oct 15;11(10):5126-5140. eCollection 2021. Am J Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34765316 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a Nomogram to Predict Cancer-Specific Survival for Middle-Aged Patients With Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Public Health. 2022 Feb 28;10:848716. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.848716. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35296046 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Livraghi T, Meloni F, Di Stasi M, Rolle E, Solbiati L, Tinelli C, Rossi S. Sustained complete response and complications rates after radiofrequency ablation of very early hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: is resection still the treatment of choice? Hepatology. 2008;47(1):82–89. doi: 10.1002/hep.21933. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

