Genome-wide association studies identify 137 genetic loci for DNA methylation biomarkers of aging
- PMID: 34187551
- PMCID: PMC8243879
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-021-02398-9
Genome-wide association studies identify 137 genetic loci for DNA methylation biomarkers of aging
Abstract
Background: Biological aging estimators derived from DNA methylation data are heritable and correlate with morbidity and mortality. Consequently, identification of genetic and environmental contributors to the variation in these measures in populations has become a major goal in the field.
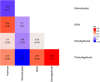
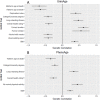
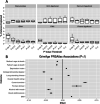
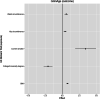
Results: Leveraging DNA methylation and SNP data from more than 40,000 individuals, we identify 137 genome-wide significant loci, of which 113 are novel, from genome-wide association study (GWAS) meta-analyses of four epigenetic clocks and epigenetic surrogate markers for granulocyte proportions and plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 levels, respectively. We find evidence for shared genetic loci associated with the Horvath clock and expression of transcripts encoding genes linked to lipid metabolism and immune function. Notably, these loci are independent of those reported to regulate DNA methylation levels at constituent clock CpGs. A polygenic score for GrimAge acceleration showed strong associations with adiposity-related traits, educational attainment, parental longevity, and C-reactive protein levels.
Conclusion: This study illuminates the genetic architecture underlying epigenetic aging and its shared genetic contributions with lifestyle factors and longevity.
Keywords: DNA methylation; Epigenetic clock; GWAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MC_UU_00007/10/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 AG060908/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL141292/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG054628/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201000021C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/S03532X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00011/6/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/S020845/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL133221/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/R023484/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 208806/Z/17/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00011/5/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/R0245065/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201000001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- C18281/A191169/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL117626/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 29019/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

