Cell entry by SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 34187722
- PMCID: PMC8180548
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2021.06.001
Cell entry by SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
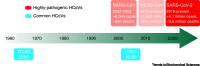
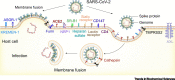
Severe acute respiratory syndrome virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) invades host cells by interacting with receptors/coreceptors, as well as with other cofactors, via its spike (S) protein that further mediates fusion between viral and cellular membranes. The host membrane protein, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), is the major receptor for SARS-CoV-2 and is a crucial determinant for cross-species transmission. In addition, some auxiliary receptors and cofactors are also involved that expand the host/tissue tropism of SARS-CoV-2. After receptor engagement, specific proteases are required that cleave the S protein and trigger its fusogenic activity. Here we discuss the recent advances in understanding the molecular events during SARS-CoV-2 entry which will contribute to developing vaccines and therapeutics.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; coreceptor; membrane fusion; receptor recognition; spike protein; virus entry.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests We declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

