Pilot Phase II Trial of Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy in Locoregionally Advanced, Resectable Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck
- PMID: 34187851
- PMCID: PMC8711237
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0585
Pilot Phase II Trial of Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy in Locoregionally Advanced, Resectable Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck
Erratum in
-
Correction: Pilot Phase II Trial of Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy in Locoregionally Advanced, Resectable Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck.Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Apr 14;28(8):1735. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-0468. Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35419587 No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: In locoregionally advanced, resectable cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (CSCC-HN), surgery followed by radiotherapy is standard but can be cosmetically and functionally devastating, and many patients will have recurrence.
Patients and methods: Newly diagnosed or recurrent stage III-IVA CSCC-HN patients amenable to curative-intent surgery received two cycles of neoadjuvant PD-1 inhibition. The primary endpoint was ORR per RECIST 1.1. Secondary endpoints included pathologic response [pathologic complete response (pCR) or major pathologic response (MPR; ≤10% viable tumor)], safety, DSS, DFS, and OS. Exploratory endpoints included immune biomarkers of response.
Results: Of 20 patients enrolled, 7 had recurrent disease. While only 6 patients [30%; 95% confidence interval (CI), 11.9-54.3] had partial responses by RECIST, 14 patients (70%; 95% CI, 45.7-88.1) had a pCR (n = 11) or MPR (n = 3). No SAEs ocurred during or after the neoadjuvant treatment. At a median follow-up of 22.6 months (95% CI, 21.7-26.1), one patient progressed and died, one died without disease, and two developed recurrence. The 12-month DSS, DFS, and OS rates were 95% (95% CI, 85.9-100), 89.5% (95% CI, 76.7-100), and 95% (95% CI, 85.9-100), respectively. Gene expression studies revealed an inflamed tumor microenvironment in patients with pCR or MPR, and CyTOF analyses demonstrated a memory CD8+ T-cell cluster enriched in patients with pCR.
Conclusions: Neoadjuvant immunotherapy in locoregionally advanced, resectable CSCC-HN is safe and induces a high pathologic response rate. Pathologic responses were associated with an inflamed tumor microenvironment.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03565783.
©2021 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests:
RF reports personal fees from Regeneron-Sanofi, Ayala Pharma, Klus Pharma, Medscape, Cellestia Biotech, Carevive, Prelude and Bicara; grants from AstraZeneca, Merck, Gennentech, Pfizer, Oropharynx Program Stiefel clinical trials, ASCO Career Development Award, and MD Anderson Khalifa Award within the past two years.
PS reports consulting, advisory roles, and/or stocks/ownership for Achelois, Apricity Health, BioAlta, Codiak BioSciences, Constellation, Dragonfly Therapeutics, Forty-Seven Inc., Hummingbird, ImaginAb, Jounce Therapeutics, Lava Therapeutics, Lytix Biopharma, Marker Therapeutics, Oncolytics, Infinity Pharma, BioNTech, Adaptive Biotechnologies, and Polaris; and owns a patent licensed to Jounce Therapeutics.
JA reports consulting, advisory roles, and/or stocks/ownership for Achelois, Apricity Health, BioAlta, Codiak BioSciences, Dragonfly Therapeutics, Forty-Seven Inc., Hummingbird, ImaginAb, Jounce Therapeutics, Lava Therapeutics, Lytix Biopharma, Marker Therapeutics, Polaris, BioNTech, and Adaptive Biotechnologies; and owns a patent licensed to Jounce Therapeutics.
BE served on advisory board for Roche/Genentech and for Seattle Genetics in the last 12 months.
NG received research funding from Regeneron. Received advisory board and consulting fees from PDS Biotechnology, Shattuck Labs, and Genzyme.
All other authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
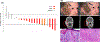


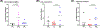
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

