Induction chemotherapy followed by definitive chemoradiotherapy versus chemoradiotherapy alone in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a randomized phase II trial
- PMID: 34188053
- PMCID: PMC8242031
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-24288-1
Induction chemotherapy followed by definitive chemoradiotherapy versus chemoradiotherapy alone in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: a randomized phase II trial
Abstract
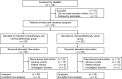
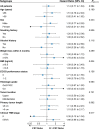
This randomized phase II trial aims to compare the efficacy and safety of induction chemotherapy followed by definitive chemoradiotherapy (CRT) versus CRT alone in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) unsuitable for surgery (N = 110). The primary outcome was overall response rate (ORR), whereas the secondary outcome was overall survival. This trial did not meet pre-specified endpoints. The ORR was 74.5% in the induction chemotherapy group versus 61.8% in the CRT alone group (P = 0.152). The 3-year overall survival rate was 41.8% in the induction chemotherapy group and 38.1% in the CRT alone group (P = 0.584; hazard ratio, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.54-1.41). Grade 3-5 adverse events were similar. Patients who responded to induction chemotherapy had improved survival in the post-hoc analysis. These results demonstrate no improvement in response rate or survival with the addition of induction chemotherapy to CRT in unselected patients with ESCC. Trial number: NCT02403531.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Bray F, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

