Taxonogenomics description of Bacillus marasmi sp. nov., a new species isolated from the stool sample
- PMID: 34188938
- PMCID: PMC8220230
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100906
Taxonogenomics description of Bacillus marasmi sp. nov., a new species isolated from the stool sample
Abstract
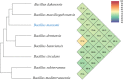
Using the culturomics method, two strains were isolated, identified, and characterised following the taxonogenomics concept. Bacillus marasmi sp. nov. strain Marseille-P3556 (= CSURP3556) is isolated from a 13-month-old girl living in Niger. The phylogenetic tree, phenotypic criteria, and genomic analysis described here clearly show that this bacterium is different from previously known bacterial species withstanding in nomenclature and new members of Bacillus genus.
Keywords: Bacillus marasmi sp. nov.; child; human stool; marasmus; taxonogenomics.
© 2021 The Authors.
Figures




References
-
- Cohn F. Untersuchungen über Bakterien. Beitrage zur Biologie der Pflanzen Heft. 1872;1:127–224.
-
- LPSN Bacillus. In: LPSN. https://lpsn.dsmz.de/genus/bacillus
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
