Influence of flaxseed with rumen undegradable protein level on milk yield, milk fatty acids and blood metabolites in transition ewes
- PMID: 34189498
- PMCID: PMC8203991
- DOI: 10.5187/jast.2021.e50
Influence of flaxseed with rumen undegradable protein level on milk yield, milk fatty acids and blood metabolites in transition ewes
Abstract
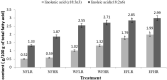
An experiment was conducted to determine the effects of two levels of rumen undegradable protein (RUP) without or with whole or extruded flaxseed on milk yield, milk component, milk fatty acids (FAs) profile and plasma metabolites in transition ewes. Three weeks before and after lambing, seventy-two Baluchi ewes were used in a completely randomized design with a 3 × 2 factorial arrangement of treatments. The treatments contained 1) no flaxseed + 20% RUP (no flaxseed, low RUP [NFLR]); 2) no flaxseed + 40% RUP (no flaxseed, high RUP [NFHR]); 3) 10% whole flaxseed + 20% RUP (whole flaxseed, low RUP [WFLR]); 4) 10% whole flaxseed + 40% RUP (whole flaxseed, high RUP [WFHR]); 5) 10% extruded flaxseed + 20% RUP (extruded flaxseed, low RUP [EFLR]), and 6) 10% extruded flaxseed + 40% RUP (extruded flaxseed, high RUP [EFHR]). Ewes fed 10% extruded flaxseed exhibited higher (p < 0.001) dry matter intake (DMI) and colostrum yield (p < 0.1) compared to other treatments. Two types of flaxseed and RUP levels had no significant effect on milk yield, but milk fat and protein contents decreased and increased in diets containing 40% RUP, respectively. Ewes fed extruded flaxseed produced milk with lower concentrations of saturated fatty acids (SFA) and higher α-linolenic and linoleic acids and also polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) compared to other groups (p < 0.05). During post-lambing, the ewes fed diets containing flaxseed exhibited higher concentration of serum non-esterified FAs (NEFA) compared to diets without flaxseed (p < 0.01). The concentration of serum β-hydroxybutyric acid (BHBA) decreased in the diets containing flaxseed types at pre-lambing, but increased in diets containing extruded flaxseed at post-lambing (p < 0.01). The serum glucose concentration of ewes (pre and post-lambing) which consumed diets containing extruded flaxseed or 40% RUP increased, but blood urea concentration was elevated following supplementation of diet with whole flaxseed or 40% RUP (p < 0.001). In conclusion, utilization of 10% extruded flaxseed in the diets of transition ewes had positive effects on animal performance with favorable changes in milk FAs profile. However, there is no considerable advantage to supply more than 20% RUP level in the diet of transition dairy sheep.
Keywords: Colostrum; Flaxseed; Milk fatty acids; Rumen undegradable protein; Transition period.
© Copyright 2021 Korean Society of Animal Science and Technology.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Dawson LER, Carson AF, Kilpatrick DJ. The effect of digestible undegradable protein concentration of concentrates and protein source offered to ewes in late pregnancy on colostrum production and lamb performance. Anim Feed Sci Technol. 1999;82:21–36. doi: 10.1016/S0377-8401(99)00101-7. - DOI
-
- Petit HV. Review: feed intake, milk production and milk composition of dairy cows fed flaxseed. Can J Anim Sci. 2010;90:115–27. doi: 10.4141/CJAS09040. - DOI
-
- Petit HV, Benchaar C. Milk production, milk composition, blood composition and conception rate of transition dairy cows fed different profiles of fatty acids. Can J Anim Sci. 2007;87:591–600. doi: 10.4141/CJAS07027. - DOI
-
- Petit HV, Côrtes C. Milk production and composition, milk fatty acid profile, and blood composition of dairy cows fed whole or ground flaxseed in the first half of lactation. J Anim Feed Sci Technol. 2010;158:36–43. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2010.03.013. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

