CARMA3 Transcriptional Regulation of STMN1 by NF-κB Promotes Renal Cell Carcinoma Proliferation and Invasion
- PMID: 34190011
- PMCID: PMC8256254
- DOI: 10.1177/15330338211027915
CARMA3 Transcriptional Regulation of STMN1 by NF-κB Promotes Renal Cell Carcinoma Proliferation and Invasion
Abstract
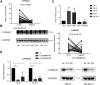
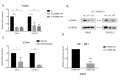
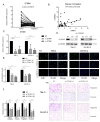
CARD-containing MAGUK protein 3 (CARMA3) is associated with tumor occurrence and progression. However, the signaling pathways involved in CARMA3 function remain unclear. We aimed to analyze the association between CARMA3 and stathmin (STMN1) through the NF-κB pathway, which is associated with cell proliferation and invasion, in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). We evaluated the effects of CARMA3 and STMN1 expression on cell migration, proliferation, and invasion in various cell lines, and their expression in tissue samples from patients with ccRCC. CARMA3 was highly expressed in ccRCC tissues and cell lines. Moreover, CARMA3 promoted the proliferation and invasion of RCC cells by activating the NF-κB pathway to transcribe STMN1. Stathmin exhibited a consistent profile with CARMA3 in ccRCC tissue, and could be an effector for CARMA3-activated cell proliferation and invasion of ccRCC cells. In summary, CARMA3 may serve as a promising target for ccRCC treatment.
Keywords: CARMA3; STMN1; renal cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

