Forty Years of Oxalobacter formigenes, a Gutsy Oxalate-Degrading Specialist
- PMID: 34190610
- PMCID: PMC8388816
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00544-21
Forty Years of Oxalobacter formigenes, a Gutsy Oxalate-Degrading Specialist
Abstract
Oxalobacter formigenes, a unique anaerobic bacterium that relies solely on oxalate for growth, is a key oxalate-degrading bacterium in the mammalian intestinal tract. Degradation of oxalate in the gut by O. formigenes plays a critical role in preventing renal toxicity in animals that feed on oxalate-rich plants. The role of O. formigenes in reducing the risk of calcium oxalate kidney stone disease and oxalate nephropathy in humans is less clear, in part due to difficulties in culturing this organism and the lack of studies which have utilized diets in which the oxalate content is controlled. Herein, we review the literature on the 40th anniversary of the discovery of O. formigenes, with a focus on its biology, its role in gut oxalate metabolism and calcium oxalate kidney stone disease, and potential areas of future research. Results from ongoing clinical trials utilizing O. formigenes in healthy volunteers and in patients with primary hyperoxaluria type 1 (PH1), a rare but severe form of calcium oxalate kidney stone disease, are also discussed. Information has been consolidated on O. formigenes strains and best practices to culture this bacterium, which should serve as a good resource for researchers.
Keywords: Oxalobacter formigenes; culture methods; gut microbiome; kidney stone disease; oxalate degradation; probiotics.
Figures

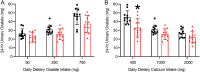
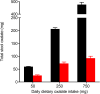
Similar articles
-
Oxalobacter formigenes produces metabolites and lipids undetectable in oxalotrophic Bifidobacterium animalis.Metabolomics. 2020 Nov 21;16(12):122. doi: 10.1007/s11306-020-01747-2. Metabolomics. 2020. PMID: 33219444
-
Association of intestinal oxalate-degrading bacteria with recurrent calcium kidney stone formation and hyperoxaluria: a case-control study.BJU Int. 2020 Jan;125(1):133-143. doi: 10.1111/bju.14840. Epub 2019 Aug 18. BJU Int. 2020. PMID: 31145528
-
Oxalobacter formigenes and its role in oxalate metabolism in the human gut.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2004 Jan 15;230(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1097(03)00864-4. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2004. PMID: 14734158 Review.
-
The genetic composition of Oxalobacter formigenes and its relationship to colonization and calcium oxalate stone disease.Urolithiasis. 2013 Jun;41(3):187-96. doi: 10.1007/s00240-013-0566-7. Epub 2013 Apr 30. Urolithiasis. 2013. PMID: 23632911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intestinal Oxalobacter formigenes colonization in calcium oxalate stone formers and its relation to urinary oxalate.J Endourol. 2003 Apr;17(3):173-6. doi: 10.1089/089277903321618743. J Endourol. 2003. PMID: 12803990
Cited by
-
Engineered microorganisms: A new direction in kidney stone prevention and treatment.Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2024 Mar 8;9(2):294-303. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2024.02.005. eCollection 2024 Jun. Synth Syst Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38510204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing inter-kingdom metabolic disparities at the human-fungal interface for novel therapeutic approaches.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Apr 24;11:1386598. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1386598. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38721278 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of calcium oxalate kidney stones: A comprehensive analysis of clinical and gut microbiome characteristics.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jul 18;104(29):e43103. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000043103. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40696591 Free PMC article.
-
Postbiotics and Kidney Disease.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Sep 6;14(9):623. doi: 10.3390/toxins14090623. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36136562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New perspectives on an old grouping: The genomic and phenotypic variability of Oxalobacter formigenes and the implications for calcium oxalate stone prevention.Front Microbiol. 2022 Dec 21;13:1011102. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1011102. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36620050 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morris M, Garcia-Rivera J. 1955. The destruction of oxalates by the rumen contents of cows. J Dairy Sci 38:1169. 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(55)95091-8. - DOI
-
- Talapatra S, Ray S, Sen K. 1948. Calcium assimilation in ruminants on oxalate-rich diet. J Agric Sci 38:163–173. 10.1017/S0021859600005426. - DOI
-
- Hodgkinson A. 1977. Oxalic acid in biology and medicine. Academic Press, New York, NY.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

