Gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumor of the accessory papilla of the duodenum: a case report
- PMID: 34191176
- PMCID: PMC8245605
- DOI: 10.1186/s40792-021-01241-4
Gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumor of the accessory papilla of the duodenum: a case report
Abstract
Background: Contrary to the increasing incidence of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (GEP-NETs), GEP-NETs of the accessory papilla of the duodenum are extremely rare. Furthermore, there have been no recommendations regarding the treatment strategy for GEP-NETs of the accessory papilla of the duodenum. We present a case of GEP-NET of the accessory papilla of the duodenum successfully treated with robotic pancreatoduodenectomy.
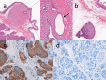
Case presentation: A case of a 70-year-old complaining of no symptoms was diagnosed with GEP-NET of the accessory papilla of the duodenum. A 8-mm tumor was located at the submucosal layer with a biopsy demonstrating a neuroendocrine tumor grade 1. The patient underwent robotic pancreatoduodenectomy as curative resection for the tumor. The total operative time was 406 min with an estimated blood loss of 150 mL. The histological examination revealed a well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumor with low Ki-67 index (< 1%). In the posterior areas of the pancreas, the lymph node metastases were detected. The patient was followed up for 6 months with no recurrence postoperatively.
Conclusions: Considering the potential risks of the lymph node metastases, the standard treatment strategy for GEP-NETs of the accessory papilla of the duodenum should be radical resection with pancreatoduodenectomy. Minimally invasive approach can be the alternative to the conventional open surgery.
Keywords: Accessory papilla of the duodenum; Carcinoid tumor; Neuroendocrine tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neuroendocrine tumor of the minor duodenal papilla with lymph node metastasis: a case report and literature review.Int Cancer Conf J. 2023 Jul 30;12(4):255-262. doi: 10.1007/s13691-023-00624-8. eCollection 2023 Oct. Int Cancer Conf J. 2023. PMID: 37577347 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumor: A case report and review of the literature.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Sep;98(37):e17154. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000017154. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31517859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A case of acinar cell carcinoma originating from the accessory papilla of the duodenum.Surg Case Rep. 2024 Apr 16;10(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s40792-024-01872-3. Surg Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38625458 Free PMC article.
-
A 12-mm carcinoid tumor of the minor duodenal papilla with lymph node metastases.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2013 Jan;43(1):74-7. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hys185. Epub 2012 Nov 6. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23136240
-
Gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine (carcinoid) tumors in children.Semin Pediatr Surg. 2014 Apr;23(2):91-5. doi: 10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2014.03.007. Epub 2014 Mar 14. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2014. PMID: 24931354 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroendocrine tumor of the minor duodenal papilla with lymph node metastasis: a case report and literature review.Int Cancer Conf J. 2023 Jul 30;12(4):255-262. doi: 10.1007/s13691-023-00624-8. eCollection 2023 Oct. Int Cancer Conf J. 2023. PMID: 37577347 Free PMC article.
-
Usefulness of Endoscopic Mucosal Resection Using an Over-the-Scope Clip for Duodenal Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Multicenter Retrospective Comparative Study.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Aug;40(8):2018-2027. doi: 10.1111/jgh.17005. Epub 2025 May 23. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 40406930 Free PMC article.
-
A case of neuroendocrine neoplasm of the minor duodenal papilla.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2023 Apr;16(2):171-179. doi: 10.1007/s12328-022-01739-w. Epub 2022 Dec 21. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 36542298 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

