Autopsy of COVID-19 patients in China
- PMID: 34192086
- PMCID: PMC7313767
- DOI: 10.1093/nsr/nwaa123
Autopsy of COVID-19 patients in China
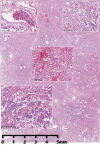
Figures

References
-
- Yao XH, Li TY, He ZCet al. . Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 2020; 49: 411–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
