CovidGAN: Data Augmentation Using Auxiliary Classifier GAN for Improved Covid-19 Detection
- PMID: 34192100
- PMCID: PMC8043420
- DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2994762
CovidGAN: Data Augmentation Using Auxiliary Classifier GAN for Improved Covid-19 Detection
Abstract
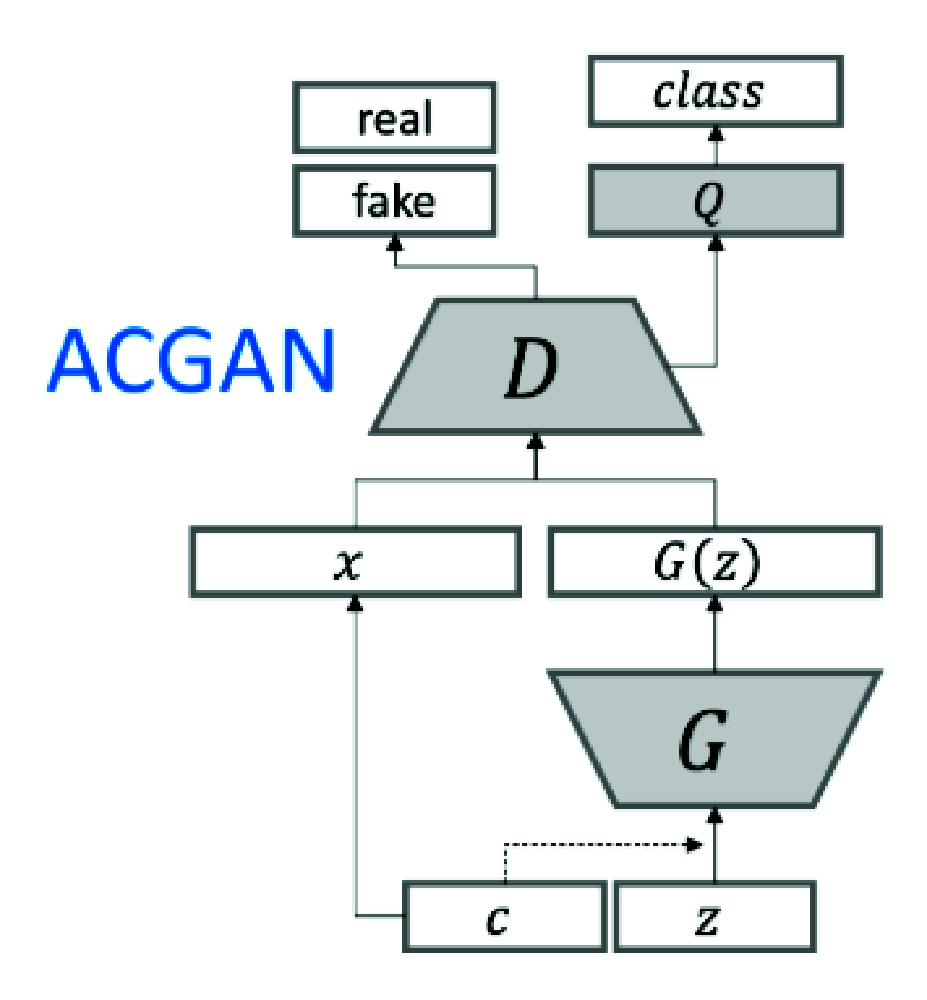
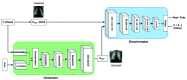
Coronavirus (COVID-19) is a viral disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The spread of COVID-19 seems to have a detrimental effect on the global economy and health. A positive chest X-ray of infected patients is a crucial step in the battle against COVID-19. Early results suggest that abnormalities exist in chest X-rays of patients suggestive of COVID-19. This has led to the introduction of a variety of deep learning systems and studies have shown that the accuracy of COVID-19 patient detection through the use of chest X-rays is strongly optimistic. Deep learning networks like convolutional neural networks (CNNs) need a substantial amount of training data. Because the outbreak is recent, it is difficult to gather a significant number of radiographic images in such a short time. Therefore, in this research, we present a method to generate synthetic chest X-ray (CXR) images by developing an Auxiliary Classifier Generative Adversarial Network (ACGAN) based model called CovidGAN. In addition, we demonstrate that the synthetic images produced from CovidGAN can be utilized to enhance the performance of CNN for COVID-19 detection. Classification using CNN alone yielded 85% accuracy. By adding synthetic images produced by CovidGAN,the accuracy increased to 95%. We hope this method will speed up COVID-19 detection and lead to more robust systems of radiology.
Keywords: COVID-19 detection; Deep learning; convolutional neural networks; generative adversarial networks; synthetic data augmentation.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License. For more information, see https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Generation of Synthetic Chest X-ray Images and Detection of COVID-19: A Deep Learning Based Approach.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 May 18;11(5):895. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11050895. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34069841 Free PMC article.
-
Data augmentation using Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) for GAN-based detection of Pneumonia and COVID-19 in chest X-ray images.Inform Med Unlocked. 2021;27:100779. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2021.100779. Epub 2021 Nov 22. Inform Med Unlocked. 2021. PMID: 34841040 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning Algorithm for COVID-19 Classification Using Chest X-Ray Images.Comput Math Methods Med. 2021 Nov 9;2021:9269173. doi: 10.1155/2021/9269173. eCollection 2021. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021. PMID: 34795794 Free PMC article.
-
Generative adversarial network based data augmentation for CNN based detection of Covid-19.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 10;12(1):19186. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23692-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36357530 Free PMC article.
-
Development and integration of VGG and dense transfer-learning systems supported with diverse lung images for discovery of the Coronavirus identity.Inform Med Unlocked. 2022;32:101004. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2022.101004. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Inform Med Unlocked. 2022. PMID: 35822170 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Towards smart diagnostic methods for COVID-19: Review of deep learning for medical imaging.IPEM Transl. 2022 Nov-Dec;3:100008. doi: 10.1016/j.ipemt.2022.100008. Epub 2022 Oct 26. IPEM Transl. 2022. PMID: 36312890 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Artificial Intelligence for Screening COVID-19 Patients Using Digital Images: Meta-analysis.JMIR Med Inform. 2021 Apr 29;9(4):e21394. doi: 10.2196/21394. JMIR Med Inform. 2021. PMID: 33764884 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-texture features and optimized DeepNet for COVID-19 detection using chest x-ray images.Concurr Comput. 2022 Oct 10;34(22):e7157. doi: 10.1002/cpe.7157. Epub 2022 Aug 1. Concurr Comput. 2022. PMID: 36246408 Free PMC article.
-
Radiological Analysis of COVID-19 Using Computational Intelligence: A Broad Gauge Study.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Feb 23;2022:5998042. doi: 10.1155/2022/5998042. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. PMID: 35251572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 prediction through X-ray images using transfer learning-based hybrid deep learning approach.Mater Today Proc. 2022;51:2520-2524. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2021.12.123. Epub 2021 Dec 13. Mater Today Proc. 2022. PMID: 34926174 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang S., Sun J., Mehmood I., Pan C., Chen Y., and Zhang Y., “Cerebral micro-bleeding identification based on a nine-layer convolutional neural network with stochastic pooling,” Concurrency Comput., Pract. Exper., vol. 32, no. , p. e5130, Jan. 2020.
-
- Litjens G., Kooi T., Bejnordi B. E., Setio A. A. A., Ciompi F., Ghafoorian M., van der Laak J. A. W. M., van Ginneken B., and Sánchez C. I., “A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis,” Med. Image Anal., vol. 42, pp. 60–88, Dec. 2017. - PubMed
-
- Roth H. R., Lu L., Liu J., Yao J., Seff A., Cherry K., Kim L., and Summers R. M., “Improving computer-aided detection using convolutional neural networks and random view aggregation,” IEEE Trans. Med. Imag., vol. 35, no. 5, pp. 1170–1181, May 2016, doi: 10.1109/tmi.2015.2482920. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
