Comprehensive Proteomics Profiling Reveals Circulating Biomarkers of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 34192899
- PMCID: PMC8292216
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.120.007849
Comprehensive Proteomics Profiling Reveals Circulating Biomarkers of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
Background: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is caused by mutations in the genes coding for proteins essential in normal myocardial contraction. However, it remains unclear through which molecular pathways gene mutations mediate the development of HCM. The objectives were to determine plasma protein biomarkers of HCM and to reveal molecular pathways differentially regulated in HCM.
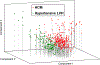
Methods: We conducted a multicenter case-control study of cases with HCM and controls with hypertensive left ventricular hypertrophy. We performed plasma proteomics profiling of 1681 proteins. We performed a sparse partial least squares discriminant analysis to develop a proteomics-based discrimination model with data from 1 institution (ie, the training set). We tested the discriminative ability in independent samples from the other institution (ie, the test set). As an exploratory analysis, we executed pathway analysis of significantly dysregulated proteins. Pathways with false discovery rate <0.05 were declared positive.
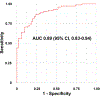
Results: The study included 266 cases and 167 controls (n=308 in the training set; n=125 in the test set). Using the proteomics-based model derived from the training set, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve was 0.89 (95% CI, 0.83-0.94) in the test set. Pathway analysis revealed that the Ras-MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) pathway, along with its upstream and downstream pathways, was upregulated in HCM. Pathways involved in inflammation and fibrosis-for example, the TGF (transforming growth factor)-β pathway-were also upregulated.
Conclusions: This study serves as the largest-scale investigation with the most comprehensive proteomics profiling in HCM, revealing circulating biomarkers and exhibiting both novel (eg, Ras-MAPK) and known (eg, TGF-β) pathways differentially regulated in HCM.
Keywords: biomarkers; cardiomyopathies; hypertrophy; mutation; proteomics.
Figures

Comment in
-
Letter by Luo and Bu Regarding Article, "Comprehensive Proteomics Profiling Reveals Circulating Biomarkers of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy".Circ Heart Fail. 2022 Jun;15(6):e009499. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.122.009499. Epub 2022 Apr 20. Circ Heart Fail. 2022. PMID: 35440167 No abstract available.
-
Response by Liang and Shimada to Letter Regarding Article "Comprehensive Proteomics Profiling Reveals Circulating Biomarkers of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy".Circ Heart Fail. 2022 Jun;15(6):e009568. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.122.009568. Epub 2022 Apr 20. Circ Heart Fail. 2022. PMID: 35727883 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Maron BJ. Clinical course and management of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:655–668. - PubMed
-
- Maron BJ, Doerer JJ, Haas TS, Tierney DM, Mueller FO. Sudden deaths in young competitive athletes: analysis of 1866 deaths in the United States, 1980–2006. Circulation. 2009;119:1085–1092. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

