Platelet-rich plasma regulating the repair of ultraviolet B-induced acute tissue inflammation: adjusting macrophage polarization through the activin receptor-follistatin system
- PMID: 34193023
- PMCID: PMC8806634
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1944026
Platelet-rich plasma regulating the repair of ultraviolet B-induced acute tissue inflammation: adjusting macrophage polarization through the activin receptor-follistatin system
Abstract
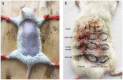
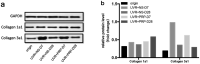
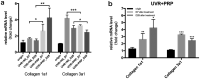
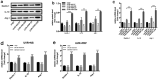
Ultraviolet B (UVB) is one of the most common exogenous factors in skin aging, especially photoaging. Once a large amount of UVB accumulates within a short period of time, skin tissue can become inflamed. It has also been found in clinics that platelet-rich plasma (PRP) can promote wound repair; therefore, the aim of this study was to identify the mechanism by which PRP repairs UVB-induced skin photodamage. We used PRP of Sprague-Dawley rats with the two-spin technique in the established acute UVB radiation photodamage model and harvested the corresponding skin after 1, 7, and 28 d. Hematoxylin and eosin staining was used to observe tissue inflammation. We found that PRP reduces inflammation in the early stages of UVB-induced acute skin damage, and then promotes the proliferation of collagen in the middle and late stages. Moreover, PRP can stimulate Act A and M1 polarization in the early stage, while inhibiting activin A (Act A) and inducing M2 polarization in the middle and late stages. In conclusion, this study demonstrates that PRP plays an important regulatory role in helping reduce UVB-induced acute skin tissue inflammation by adjusting macrophage polarization, which alleviates skin inflammation and stimulates collagen regeneration.
Keywords: Platelet-rich plasma; UVB-induced acute photodamage; activin; inflammation; macrophage polarization.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures




References
-
- Hatakeyama M, Fukunaga A, Washio K, et al. Anti-inflammatory role of langerhans cells and apoptotic keratinocytes in ultraviolet-b-induced cutaneous inflammation. J Immunol. 2017;199(8):2937–2947. . - PubMed
-
- Phillips DJ, de Kretser DM, Hedger MP.. Activin and related proteins in inflammation: not just interested bystanders. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009;20(2):153–164. - PubMed
-
- Karagiannidis C, Hense G, Martin C, et al. Activin A is an acute allergen-responsive cytokine and provides a link to TGF-beta-mediated airway remodeling in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117(1):111–118. . - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
