BCL-xL is correlated with disease severity in neonatal infants with early sepsis
- PMID: 34193088
- PMCID: PMC8243905
- DOI: 10.1186/s12887-021-02764-3
BCL-xL is correlated with disease severity in neonatal infants with early sepsis
Abstract
Background: Sepsis is the most common cause of morbidity and mortality in neonatal infants. It is essential to find an accurate and sensitive biomarker to confirm and treat neonatal sepsis in order to decrease the rate of mortality. The aim of this study was to investigate the association between disease severity in patients with sepsis and TNF-α, B cell lymphoma-extra-large (BCL-xL), and serum Mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP).
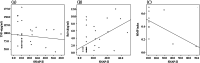
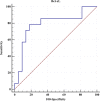
Methods: We investigated the correlation between SNAP-II score and levels of TNF-α, BCL-xL, and MMP-index, respectively. The receiver-operating characteristics (ROC) was to assess the diagnostic value of the the Bcl-xL in the diagnosis of the of septic shock.
Results: A total of 37 infants were diagnosed with sepsis. SNAP-II was positively correlated with the level of BCL-xL (r = 0.450, P = 0.006). The area under the BCL-xL curve was 83.0 %, and the 95 % CI was 67.1-93.3 %. The septic shock threshold was > 3.022 ng/mL, and the sensitivity and specificity were 75.0 and 95.2 %, respectively. The positive predictive value was 92.3 %, and the negative predictive value was 83.3 %. Furthermore, the level of SNAP-II was > 10, and BCL-xL was > 3.022 ng/mL as the threshold, and the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of septic shock were 93.8 %, 95.2 %, 93.8 %, and 95.2 %, respectively.
Conclusions: BCL-xL is associated with the progression of sepsis. The combination of BCL-xL and SNAP-II could be early predicte the severity of the disease.
Keywords: BCL-xL; Neonatal critical illness score; Receiver operator characteristic curve; Sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Combined prognostic value of serum lactic acid, procalcitonin and severity score for short-term prognosis of septic shock patients].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021 Mar;33(3):281-285. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20201113-00715. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021. PMID: 33834968 Chinese.
-
[The value of pro-adrenomedullin in early diagnosis of sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015 Sep;27(9):739-42. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015. PMID: 26955700 Chinese.
-
[Significance of high mobility group box 1, von Willebrand factor and other cytokines in the evaluation of severity and prognosis of sepsis patients].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Aug;32(8):933-937. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200428-00346. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 32912405 Chinese.
-
Role of procalcitonin, C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, interleukin-8 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis.Turk J Pediatr. 2007 Jan-Mar;49(1):7-20. Turk J Pediatr. 2007. PMID: 17479639
-
[Value of blood ammonia on predicting the severity and prognosis of patients with sepsis: a prospective observation study].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Nov;32(11):1315-1319. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200305-00210. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 33463489 Chinese.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

