Effect modification of the association between comorbidities and severe course of COVID-19 disease by age of study participants: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 34193261
- PMCID: PMC8244460
- DOI: 10.1186/s13643-021-01732-3
Effect modification of the association between comorbidities and severe course of COVID-19 disease by age of study participants: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Comprehensive evidence synthesis on the associations between comorbidities and behavioural factors with hospitalisation, intensive care unit (ICU) admission, and death due to COVID-19 is required for deriving national and international recommendations on primary targets for non-pharmacological interventions (NPI) and vaccination strategies.
Methods: We performed a rapid systematic review and meta-analysis on studies and publicly accessible data to quantify associations between predisposing health conditions, demographics, behavioural factors on the one hand and hospitalisation, ICU admission, and death from COVID-19 on the other hand. We provide ranges of reported and calculated effect estimates and pooled relative risks derived from a meta-analysis and meta-regression.
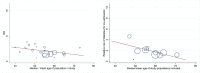
Results: Seventy-five studies were included in qualitative and 74 in quantitative synthesis, with study populations ranging from 19 to 44,672 COVID-19 cases. The risk of dying from COVID-19 was significantly associated with cerebrovascular [pooled relative risk (RR) 2.7 (95% CI 1.7-4.1)] and cardiovascular [RR 3.2 (CI 2.3-4.5)] diseases, hypertension [RR 2.6 (CI 2.0-3.4)], and renal disease [RR 2.5 (CI 1.8-3.4)], with high heterogeneity in pooled estimates, partly but not solely explained by age of study participants. For some comorbidities, our meta-regression showed a decrease in effect on the severity of disease with a higher median age of the study population. Compared to death, associations between several comorbidities and hospitalisation and ICU admission were less pronounced.
Conclusions: We obtained robust estimates on the magnitude of risk for COVID-19 hospitalisation, ICU admission, and death associated with comorbidities, demographic, and behavioural risk factors and show that these estimates are modified by age of study participants. This interaction is an important finding to be kept in mind for current vaccination strategies and for the protection of individuals with high risk for a severe COVID-19 course.
Keywords: COVID-19-associated hospitalisation; COVID-19-associated mortality; Comorbidity; Effect modification; Interaction; Meta-analyses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Chen Q, Zheng Z, Zhang C, Zhang X, Wu H, Wang J, et al. Clinical characteristics of 145 patients with corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Taizhou, Zhejiang, China. Infection. 2020;48(4):543–51. Available from: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s15010-020-01432-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang R, Pan M, Zhang X, Han M, Fan X, Zhao F, et al. Epidemiological and clinical features of 125 Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 in Fuyang, Anhui, China. Int J Infect Dis. 2020;95:421–8. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1201971220302034. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zheng F, Tang W, Li H, Huang YX, Xie YL, Zhou ZG. Clinical characteristics of 161 cases of corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Changsha. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(6):3404–3410. - PubMed
-
- Li X, Xu S, Yu M, Wang K, Tao Y, Zhou Y, et al. Risk factors for severity and mortality in adult COVID-19 inpatients in Wuhan. J Allergy Clin Immuno. 2020;146(1):110–8. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0091674920304954. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

