The Complex Formed by Group I Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor (mGluR) and Homer1a Plays a Central Role in Metaplasticity and Homeostatic Synaptic Scaling
- PMID: 34193623
- PMCID: PMC8244974
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0026-21.2021
The Complex Formed by Group I Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor (mGluR) and Homer1a Plays a Central Role in Metaplasticity and Homeostatic Synaptic Scaling
Abstract
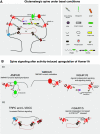
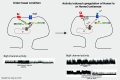
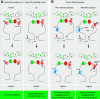
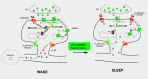
G-protein-coupled receptors can be constitutively activated following physical interaction with intracellular proteins. The first example described was the constitutive activation of Group I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR: mGluR1,5) following their interaction with Homer1a, an activity-inducible early-termination variant of the scaffolding protein Homer that lacks dimerization capacity (Ango et al., 2001). Homer1a disrupts the links, maintained by the long form of Homer (cross-linking Homers), between mGluR1,5 and the Shank-GKAP-PSD-95-ionotropic glutamate receptor network. Two characteristics of the constitutive activation of the Group I mGluR-Homer1a complex are particularly interesting: (1) it affects a large number of synapses in which Homer1a is upregulated following enhanced, long-lasting neuronal activity; and (2) it mainly depends on Homer1a protein turnover. The constitutively active Group I mGluR-Homer1a complex is involved in the two main forms of non-Hebbian neuronal plasticity: "metaplasticity" and "homeostatic synaptic scaling," which are implicated in a large series of physiological and pathologic processes. Those include non-Hebbian plasticity observed in visual system, synapses modulated by addictive drugs (rewarded synapses), chronically overactivated synaptic networks, normal sleep, and sleep deprivation.
Copyright © 2021 the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Homeostatic scaling requires group I mGluR activation mediated by Homer1a.Neuron. 2010 Dec 22;68(6):1128-42. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.11.008. Neuron. 2010. PMID: 21172614 Free PMC article.
-
Homer1a and mGluR1/5 Signaling in Homeostatic Sleep Drive and Output.Yale J Biol Med. 2019 Mar 25;92(1):93-101. eCollection 2019 Mar. Yale J Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30923476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Homer1a signaling in the amygdala counteracts pain-related synaptic plasticity, mGluR1 function and pain behaviors.Mol Pain. 2011 May 19;7:38. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-7-38. Mol Pain. 2011. PMID: 21595930 Free PMC article.
-
Visual experience regulates metabotropic glutamate receptor-mediated plasticity of AMPA receptor synaptic transmission by homer1a induction.J Neurosci. 2006 Jul 19;26(29):7575-80. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5083-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16855085 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Stress-Induced Changes of Homer1 Expression in Stress Susceptibility.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2021 Jun;86(6):613-626. doi: 10.1134/S0006297921060018. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2021. PMID: 34225586 Review.
Cited by
-
Postsynaptic Proteins at Excitatory Synapses in the Brain-Relationship with Depressive Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 28;23(19):11423. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911423. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specific pharmacological and Gi/o protein responses of some native GPCRs in neurons.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 5;15(1):1990. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46177-z. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38443355 Free PMC article.
-
DNA2 knockout aggravates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by reducing postsynaptic Homer1a.Zool Res. 2025 Jan 18;46(1):87-102. doi: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2024.269. Zool Res. 2025. PMID: 39846189 Free PMC article.
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) in epileptogenesis: an update on abnormal mGluRs signaling and its therapeutic implications.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Feb;19(2):360-368. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.379018. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 37488891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phase separation-mediated actin bundling by the postsynaptic density condensates.Elife. 2023 Jun 15;12:e84446. doi: 10.7554/eLife.84446. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37318128 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ade KK, Wan Y, Hamann HC, O'Hare JK, Guo W, Quian A, Kumar S, Bhagat S, Rodriguiz RM, Wetsel WC, Conn PJ, Dzirasa K, Huber KM, Calakos N (2016) Increased metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 signaling underlies obsessive-compulsive disorder-like behavioral and striatal circuit abnormalities in mice. Biol Psychiatry 80:522–533. 10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.04.023 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
