Preventive effect of Ninjin-yoei-to, a Kampo medicine, on amyloid β1-42-induced neurodegeneration via intracellular Zn2+ toxicity in the dentate gyrus
- PMID: 34193681
- PMCID: PMC8614007
- DOI: 10.1538/expanim.21-0044
Preventive effect of Ninjin-yoei-to, a Kampo medicine, on amyloid β1-42-induced neurodegeneration via intracellular Zn2+ toxicity in the dentate gyrus
Abstract
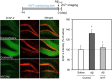
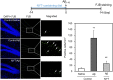
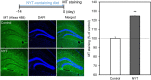
Ninjin-yoei-to (NYT), a Kampo medicine, has ameliorative effects on cognitive dysfunction via enhancing cholinergic neuron activity. To explore an efficacy of NYT administration for prevention and cure of Alzheimer's disease, here we examined the effect of NYT on amyloid β1-42 (Aβ1-42)-induced neurodegeneration in the dentate gyrus. A diet containing 3% NYT was administered to mice for 2 weeks and human Aβ1-42 was intracerebroventricularly injected. Neurodegeneration in the dentate granule cell layer of the hippocampus, which was determined 2 weeks after the injection, was rescued by administration of the diet for 4 weeks. Aβ staining (uptake) was not modified in the dentate granule cell layer by pre-administration of the diet for 2 weeks, while Aβ1-42-induced increase in intracellular Zn2+ was reduced, suggesting that pre-administration of NYT prior to Aβ injection is effective for reducing Aβ1-42-induced Zn2+ toxicity in the dentate gyrus. As a matter of fact, Aβ1-42-induced neurodegeneration in the dentate gyrus was rescued by pre-administration of NYT. Interestingly, the level of metallothioneins, intracellular Zn2+-binding proteins, which can capture Zn2+ from Zn-Aβ1-42 complexes, was elevated in the dentate granule cell layer by pre-administration of NYT. The present study suggests that pre-administration of NYT prevents Aβ1-42-mediated neurodegeneration in the dentate gyurs by induced synthesis of metallothioneins, which reduces intracellular Zn2+ toxicity induced by Aβ1-42.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Ninjin-yoei-to; Zn2+ dysregulation; amyloid β1-42; metallothionein.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Metallothionein synthesis increased by Ninjin-yoei-to, a Kampo medicine protects neuronal death and memory loss after exposure to amyloid β1-42.J Pharm Health Care Sci. 2022 Nov 1;8(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s40780-022-00257-8. J Pharm Health Care Sci. 2022. PMID: 36316709 Free PMC article.
-
Dehydroeffusol Pprevents Amyloid β1-42-mediated Hippocampal Neurodegeneration via Reducing Intracellular Zn2+ Toxicity.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Aug;58(8):3603-3613. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02364-3. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 33770339
-
Preferential Neurodegeneration in the Dentate Gyrus by Amyloid β1-42-Induced Intracellular Zn2+Dysregulation and Its Defense Strategy.Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Apr;57(4):1875-1888. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-01853-w. Epub 2019 Dec 21. Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 31865526
-
Extracellular Zn2+-Dependent Amyloid-β1-42 Neurotoxicity in Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021 Jan;199(1):53-61. doi: 10.1007/s12011-020-02131-w. Epub 2020 Apr 13. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021. PMID: 32281074 Review.
-
Is Vulnerability of the Dentate Gyrus to Aging and Amyloid-β1-42 Neurotoxicity Linked with Modified Extracellular Zn2+ Dynamics?Biol Pharm Bull. 2018;41(7):995-1000. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b17-00871. Biol Pharm Bull. 2018. PMID: 29962410 Review.
Cited by
-
Metallothionein synthesis increased by Ninjin-yoei-to, a Kampo medicine protects neuronal death and memory loss after exposure to amyloid β1-42.J Pharm Health Care Sci. 2022 Nov 1;8(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s40780-022-00257-8. J Pharm Health Care Sci. 2022. PMID: 36316709 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moryś J, Sadowski M, Barcikowska M, Maciejewska B, Narkiewicz O. The second layer neurones of the entorhinal cortex and the perforant path in physiological ageing and Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Warsz). 1994; 54: 47–53. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

