The R2R3-type MYB transcription factor MdMYB90-like is responsible for the enhanced skin color of an apple bud sport mutant
- PMID: 34193856
- PMCID: PMC8245648
- DOI: 10.1038/s41438-021-00590-3
The R2R3-type MYB transcription factor MdMYB90-like is responsible for the enhanced skin color of an apple bud sport mutant
Abstract
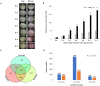
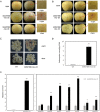
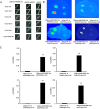
The anthocyanin content in apple skin determines its red coloration, as seen in a Fuji apple mutant. Comparative RNA-seq analysis was performed to determine differentially expressed genes at different fruit development stages between the wild-type and the skin color mutant. A novel R2R3-MYB transcription factor, MdMYB90-like, was uncovered as the key regulatory gene for enhanced coloration in the mutant. The expression of MdMYB90-like was 21.3 times higher in the mutant. MdMYB90-like regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis directly through the activation of anthocyanin biosynthesis genes and indirectly through the activation of other transcription factors that activate anthocyanin biosynthesis. MdMYB90-like bound to the promoters of both structural genes (MdCHS and MdUFGT) and other transcription factor genes (MdMYB1 and MdbHLH3) in the yeast one-hybrid system, electrophoretic mobility shift assay, and dual-luciferase assay. Transgenic analysis showed that MdMYB90-like was localized in the nucleus, and its overexpression induced the expression of other anthocyanin-related genes, including MdCHS, MdCHI, MdANS, MdUFGT, MdbHLH3, and MdMYB1. The mutant had reduced levels of DNA methylation in two regions (-1183 to -988 and -2018 to -1778) of the MdMYB90-like gene promoter, which might explain the enhanced expression of the gene and the increased anthocyanin content in the mutant apple skin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Transcriptomic Profiling of Apple Calli With a Focus on the Key Genes for ALA-Induced Anthocyanin Accumulation.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Mar 26;12:640606. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.640606. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 33841467 Free PMC article.
-
MYB_SH[AL]QKY[RF] transcription factors MdLUX and MdPCL-like promote anthocyanin accumulation through DNA hypomethylation and MdF3H activation in apple.Tree Physiol. 2021 May 14;41(5):836-848. doi: 10.1093/treephys/tpaa156. Tree Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33171489
-
Isolation and functional analysis of a MYB transcription factor gene that is a key regulator for the development of red coloration in apple skin.Plant Cell Physiol. 2007 Jul;48(7):958-70. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcm066. Epub 2007 May 26. Plant Cell Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17526919
-
The bHLH transcription factor MdbHLH3 promotes anthocyanin accumulation and fruit colouration in response to low temperature in apples.Plant Cell Environ. 2012 Nov;35(11):1884-97. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2012.02523.x. Epub 2012 May 14. Plant Cell Environ. 2012. PMID: 22519753
-
The effect of promoter methylation on MdMYB1 expression determines the level of anthocyanin accumulation in skins of two non-red apple cultivars.BMC Plant Biol. 2018 Jun 5;18(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1320-7. BMC Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 29871614 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Hypermethylation in the promoter regions of flavonoid pathway genes is associated with skin color fading during 'Daihong' apple fruit development.Hortic Res. 2024 Feb 15;11(3):uhae031. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhae031. eCollection 2024 Mar. Hortic Res. 2024. PMID: 38481937 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of R2R3-MYB Genes Response to Saline-Alkali Stress in Quinoa.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 23;24(11):9132. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119132. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298082 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses provide insights into variations in flavonoids contents between two Artemisia cultivars.BMC Plant Biol. 2023 May 30;23(1):288. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04295-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 37254042 Free PMC article.
-
Light Induced Regulation Pathway of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Plants.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 15;22(20):11116. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011116. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anthocyanin Accumulation and Molecular Analysis of Correlated Genes by Metabolomics and Transcriptomics in Sister Line Apple Cultivars.Life (Basel). 2022 Aug 16;12(8):1246. doi: 10.3390/life12081246. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36013425 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee HS, et al. Analysis of Fuji apple somatic variants from next-generation sequencing. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016;15:52–52. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 31671766/National Science Foundation of China | National Natural Science Foundation of China-Yunnan Joint Fund (NSFC-Yunnan Joint Fund)
- 31872074/National Science Foundation of China | National Natural Science Foundation of China-Yunnan Joint Fund (NSFC-Yunnan Joint Fund)
- JCYJ20190808143207457/Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission
- JCYJ20180305124101630/Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission
- JCYJ20170818094958663/Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission

