SETBP1 accumulation induces P53 inhibition and genotoxic stress in neural progenitors underlying neurodegeneration in Schinzel-Giedion syndrome
- PMID: 34193871
- PMCID: PMC8245514
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-24391-3
SETBP1 accumulation induces P53 inhibition and genotoxic stress in neural progenitors underlying neurodegeneration in Schinzel-Giedion syndrome
Abstract
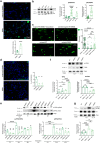
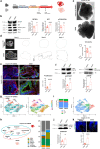
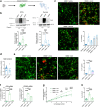
The investigation of genetic forms of juvenile neurodegeneration could shed light on the causative mechanisms of neuronal loss. Schinzel-Giedion syndrome (SGS) is a fatal developmental syndrome caused by mutations in the SETBP1 gene, inducing the accumulation of its protein product. SGS features multi-organ involvement with severe intellectual and physical deficits due, at least in part, to early neurodegeneration. Here we introduce a human SGS model that displays disease-relevant phenotypes. We show that SGS neural progenitors exhibit aberrant proliferation, deregulation of oncogenes and suppressors, unresolved DNA damage, and resistance to apoptosis. Mechanistically, we demonstrate that high SETBP1 levels inhibit P53 function through the stabilization of SET, which in turn hinders P53 acetylation. We find that the inheritance of unresolved DNA damage in SGS neurons triggers the neurodegenerative process that can be alleviated either by PARP-1 inhibition or by NAD + supplementation. These results implicate that neuronal death in SGS originates from developmental alterations mainly in safeguarding cell identity and homeostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Overlapping SETBP1 gain-of-function mutations in Schinzel-Giedion syndrome and hematologic malignancies.PLoS Genet. 2017 Mar 27;13(3):e1006683. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006683. eCollection 2017 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28346496 Free PMC article.
-
Progressive brain atrophy in Schinzel-Giedion syndrome with a SETBP1 mutation.Eur J Med Genet. 2015 Aug;58(8):369-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2015.05.006. Epub 2015 Jun 19. Eur J Med Genet. 2015. PMID: 26096993
-
A pathogenic variant in the SETBP1 hotspot results in a forme-fruste Schinzel-Giedion syndrome.Am J Med Genet A. 2020 Aug;182(8):1947-1951. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.61630. Epub 2020 May 22. Am J Med Genet A. 2020. PMID: 32445275
-
Schinzel-Giedion syndrome: a novel case, review and revised diagnostic criteria.J Genet. 2018 Mar;97(1):35-46. J Genet. 2018. PMID: 29666323 Review.
-
Novel SETBP1 D874V adjacent to the degron causes canonical schinzel-giedion syndrome: a case report and review of the literature.BMC Pediatr. 2024 May 6;24(1):309. doi: 10.1186/s12887-024-04779-y. BMC Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38711130 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Harnessing the potential of human induced pluripotent stem cells, functional assays and machine learning for neurodevelopmental disorders.Front Neurosci. 2025 Jan 8;18:1524577. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1524577. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 39844857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Balanced SET levels favor the correct enhancer repertoire during cell fate acquisition.Nat Commun. 2023 Jun 3;14(1):3212. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39043-x. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37270547 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetics in rare neurological diseases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jul 23;12:1413248. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1413248. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39108836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The landscape of SETBP1 gene expression and transcription factor activity across human tissues.PLoS One. 2024 Jan 2;19(1):e0296328. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296328. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38165902 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk of moderate ROS and PARP-1 contributes to sustainable proliferation of conditionally reprogrammed keratinocytes.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2023 Feb;37(2):e23262. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23262. Epub 2022 Nov 24. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36424367 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

