RAS-inhibiting biologics identify and probe druggable pockets including an SII-α3 allosteric site
- PMID: 34193876
- PMCID: PMC8245420
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-24316-0
RAS-inhibiting biologics identify and probe druggable pockets including an SII-α3 allosteric site
Abstract
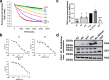
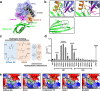
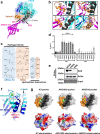
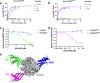
RAS mutations are the most common oncogenic drivers across human cancers, but there remains a paucity of clinically-validated pharmacological inhibitors of RAS, as druggable pockets have proven difficult to identify. Here, we identify two RAS-binding Affimer proteins, K3 and K6, that inhibit nucleotide exchange and downstream signaling pathways with distinct isoform and mutant profiles. Affimer K6 binds in the SI/SII pocket, whilst Affimer K3 is a non-covalent inhibitor of the SII region that reveals a conformer of wild-type RAS with a large, druggable SII/α3 pocket. Competitive NanoBRET between the RAS-binding Affimers and known RAS binding small-molecules demonstrates the potential to use Affimers as tools to identify pharmacophores. This work highlights the potential of using biologics with small interface surfaces to select unseen, druggable conformations in conjunction with pharmacophore identification for hard-to-drug proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
M.J. works for Avacta Life Sciences who licensed the Affimers from the University of Leeds. M.J., M.J.M., D.C.T., and A.L.T. all own personal shares in Avacta Life Sciences. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

