The evaluation of part-baked frozen bread produced from wheat flour and guar gum in the diet of celiac patients
- PMID: 34194087
- PMCID: PMC8196177
- DOI: 10.1007/s13197-020-04757-z
The evaluation of part-baked frozen bread produced from wheat flour and guar gum in the diet of celiac patients
Abstract
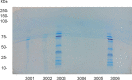
The present study evaluated an enzyme strategy for eliminating the gliadin in the flour in order to produce part-baked (PB) frozen bread for celiac patients. At first, tissue transglutaminase with lysine methyl ester transamidated the gliadin and hydrolyses gliadin protein. The deamidated dough was used for producing the PB bread and then stored as the frozen storage at - 18 °C for 15 days, followed by investigating physicochemical, rheological, and sensory properties. The SDS-PAGE result demonstrated that transamidating wheat flour with a tissue transglutaminase and L-lysine methyl ester break down the gliadin protein. The PB frozen bread with the absence of gliadin had lower specific volume, porosity, firmness, and color index (P < 0.05) but adding 0.8% guar gum could improve these factors and recompense the absence of gliadin (P < 0.05). The PB frozen bread with 0.8% guar gum had physicochemical properties such as fresh bread which produced with untreated wheat flour (P < 0.05).
Keywords: Celiac; Frozen; Gliadin; Part-baked; Rheological properties; Transdiamidation.
© Association of Food Scientists & Technologists (India) 2020.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Biochemical modifications of gliadins induced by microbial transglutaminase on wheat flour.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Nov;1830(11):5166-74. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.07.021. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23891939
-
Quality attributes and functional properties of whole wheat bread baked from frozen dough with the addition of enzymes and hydrocolloids.J Sci Food Agric. 2024 Mar 15;104(4):1928-1941. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.13077. Epub 2023 Nov 23. J Sci Food Agric. 2024. PMID: 37932850
-
Reduced-gliadin wheat bread: an alternative to the gluten-free diet for consumers suffering gluten-related pathologies.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 12;9(3):e90898. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090898. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24621595 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of waxy wheat flour and water on frozen dough and bread properties.J Food Sci. 2009 Jun;74(5):E278-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2009.01180.x. J Food Sci. 2009. PMID: 19646043
-
Microbial transglutaminase: A biotechnological tool to manage gluten intolerance.Anal Biochem. 2020 Mar 1;592:113584. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2020.113584. Epub 2020 Jan 15. Anal Biochem. 2020. PMID: 31953047 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of the effect of hydroxyl propyl methyl cellulose, pectin, and concentrated raisin juice on gluten-free bread based on rice and foxtail millet flour.Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Oct 26;12(1):439-449. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3741. eCollection 2024 Jan. Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38268869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AACC . Approved methods of the American Association of cereal chemists. 8. St. Paul: American Association of Cereal Chemists; 2000.
-
- Bárcenas ME, Rosell CM. Different approaches for increasing the shelf life of partially baked bread: low temperatures and hydrocolloid addition. Food Chem. 2007;100(4):1594–1601. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.12.043. - DOI
-
- Capriles VD, Areas JAG. Novel approaches in gluten-free breadmaking: interface between food science, nutrition, and health. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2014;13(5):871–890. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12091. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
