Stanniocalcin-1 Overexpression Prevents Depression-Like Behaviors Through Inhibition of the ROS/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 34194345
- PMCID: PMC8238083
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.644383
Stanniocalcin-1 Overexpression Prevents Depression-Like Behaviors Through Inhibition of the ROS/NF-κB Signaling Pathway
Abstract
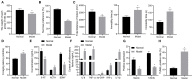
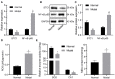
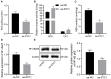
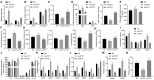
Background: Depression is a burdensome psychiatric disorder presenting with disordered inflammation and neural plasticity. We conducted this study with an aim to explore the effect of stanniocalcin-1 (STC1) on inflammation and neuron injury in rats with depression-like behaviors. Methods: A model of depression-like behaviors was established in Wistar rats by stress stimulation. Adeno-associated virus (AAV)-packaged STC1 overexpression sequence or siRNA against STC1 was introduced into rats to enhance or silence the STC1 expression. Moreover, we measured pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory proteins, superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), malondialdehyde (MDA) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. An in vitro model was induced in hippocampal neurons by CORT to explore the effect of STC1 on the neuron viability, toxicity and apoptosis. RT-qPCR and Western blot assay were employed to determine the expression of STC1 and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway-related genes. Results: STC1 was under-expressed in the hippocampus of rats with depression-like behaviors, while its overexpression could reduce the depression-like behaviors in the stress-stimulated rats. Furthermore, overexpression of STC1 resulted in enhanced neural plasticity, reduced release of pro-inflammatory proteins, elevated SOD and CAT and diminished MDA level in the hippocampus of rats with depression-like behaviors. Overexpressed STC1 blocked the ROS/NF-κB signaling pathway, thereby enhancing the viability of CORT-treated neurons while repressing their toxicity and apoptosis. Conclusion: Collectively, overexpression of STC1 inhibits inflammation and protects neuron injury in rats with depression-like behaviors by inactivating the ROS/NF-κB signaling pathway.
Keywords: NF-κB; depression; inflammation; neural plasticity; reactive oxygen species; stanniocalcin-1.
Copyright © 2021 Chao, Zhang, Pan, Zhang, Chen, Xu and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Stanniocalcin-1 Protects a Mouse Model from Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Affecting ROS-Mediated Multiple Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jul 12;17(7):1051. doi: 10.3390/ijms17071051. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27420048 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of stanniocalcin-1 inhibits the development of osteoarthritis by inhibiting survival and inflammation of fibroblast-like synovial cells.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Jun;120(6):9768-9780. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28257. Epub 2018 Dec 23. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30582210
-
Isoquercetin attenuates oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis after ischemia/reperfusion injury via Nrf2-mediated inhibition of the NOX4/ROS/NF-κB pathway.Chem Biol Interact. 2018 Mar 25;284:32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2018.02.017. Epub 2018 Feb 16. Chem Biol Interact. 2018. PMID: 29454613
-
Mammalian stanniocalcin-1 activates mitochondrial antioxidant pathways: new paradigms for regulation of macrophages and endothelium.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010 Feb;298(2):F248-54. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00260.2009. Epub 2009 Aug 5. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19656913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current research progress in the role of reactive oxygen species in esophageal adenocarcinoma.Transl Cancer Res. 2021 Mar;10(3):1568-1577. doi: 10.21037/tcr-19-1985. Transl Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35116481 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
(+)-catechin protects PC12 cells against CORT-induced oxidative stress and pyroptosis through the pathways of PI3K/AKT and Nrf2/HO-1/NF-κB.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 28;15:1450211. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1450211. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39263574 Free PMC article.
-
Itaconate inhibits corticosterone-induced necroptosis and neuroinflammation via up-regulating menin in HT22 cells.J Physiol Biochem. 2024 May;80(2):393-405. doi: 10.1007/s13105-024-01012-3. Epub 2024 Mar 1. J Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38427168
-
From inflammation to depression: key biomarkers for IBD-related major depressive disorder.J Transl Med. 2024 Nov 5;22(1):997. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05758-8. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39501335 Free PMC article.
-
STC-1 alleviates airway inflammation by regulating epithelial cell apoptosis through the 5-LO pathway.Inflammation. 2025 Aug;48(4):2152-2165. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02181-5. Epub 2024 Nov 15. Inflammation. 2025. PMID: 39546157
-
Associations of Dietary Vitamin A and Beta-Carotene Intake With Depression. A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies.Front Nutr. 2022 Apr 25;9:881139. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.881139. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35548582 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fischer Fumeaux CJ, Morisod Harari M, Weisskopf E, Eap CB, Epiney M, Vial Y, et al. . Risk-benefit balance assessment of SSRI antidepressant use during pregnancy and lactation based on best available evidence - an update. Expert Opin Drug Saf. (2019) 18:949–63. 10.1080/14740338.2019.1658740 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Maes M, Ringel K, Kubera M, Berk M, Rybakowski J. Increased autoimmune activity against 5-HT: a key component of depression that is associated with inflammation and activation of cell-mediated immunity, and with severity and staging of depression. J Affect Disord. (2012) 136:386–92. 10.1016/j.jad.2011.11.016 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

