De novo Transcriptome Sequencing Coupled With Co-expression Analysis Reveal the Transcriptional Regulation of Key Genes Involved in the Formation of Active Ingredients in Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn Under Bolting Period
- PMID: 34194480
- PMCID: PMC8236723
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2021.683037
De novo Transcriptome Sequencing Coupled With Co-expression Analysis Reveal the Transcriptional Regulation of Key Genes Involved in the Formation of Active Ingredients in Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn Under Bolting Period
Abstract
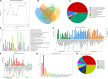
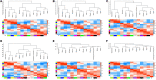
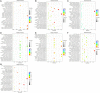
Peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn is a perennial and one-off flowering plant of the Peucedanum genus in Umbelliferae. The cultivated P. praeruptorum Dunn usually grows nutritionally in the first year and then moves into the reproductive growth in the second year. The lignification of the roots caused by bolting leads to the quality decline of crude materials. Since most of the previous studies have dealt with coumarin biosynthesis and identification of functional genes in P. praeruptorum, the scientific connotation of the inability that the bolted P. praeruptorum cannot be used medically is still unclear. Here, we employed a transcriptome sequencing combined with coexpression analysis to unearth the regulation mechanism of key genes related to coumarin synthesis in pre- and postbolting period, and to explore the mechanisms underlying the effects of bolting on the formation and transport of coumarins between the annual and biennial plants. Six cDNA libraries were constructed, and the transcripts were sequenced and assembled by Illumina Hiseq platform. A total of 336,505 unigenes were obtained from 824,129 non-redundant spliced transcripts. Unigenes (114,488) were annotated to the NCBI nr database, 119,017 and 10,475 unigenes were aligned to Gene Ontology (GO) functional groups and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways, respectively. Differential expression analysis screened out a series of upregulated and downregulated genes related to the phenylpropanoid pathway. The heatmap clustering showed that the similar expression patterns were both observed in groups C vs. D and groups C vs. F. The WGCNA-based coexpression was performed to elucidate the module and trait relationship to unearth important genes related to the bolting process. Seven pivotal modules on the KEGG functional annotations suggested these genes were mainly enriched in the process of plant-pathogen interaction, plant hormone signal transduction, MAPK signaling pathway, α-linolenic acid metabolism, circadian rhythm, and phenylpropanoid pathway. Further analysis provided clues that the key genes of the phenylpropanoid pathway, the ABC transporters, the apoptosis-related and circadian rhythm regulatory genes may play pivotal roles in regulating bolting signaling, biosynthesis, and transportation of coumarins.
Keywords: Peucedanum praeruptorum; bolting period; coexpression analysis; coumarins; key gene; transcriptional regulation.
Copyright © 2021 Song, Li, Jia, Liu, Ou and Han.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The handling editor declared a past collaboration with one of the authors CS.
Figures








References
-
- Chen L. L., Chu S. S., Zhang L., Xie J., Dai M., Wu X., et al. (2019). Tissue-specific metabolite profiling on the different parts of bolting and unbolting peucedanum praeruptorum Dunn (Qianhu) by laser microdissection combined with UPLC-Q/TOF-MS and HPLC-DAD. Molecules 24:1439. 10.3390/molecules24071439 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

