TERT and its binding protein: overexpression of GABPA/B in high grade gliomas
- PMID: 34194624
- PMCID: PMC8238242
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.27985
TERT and its binding protein: overexpression of GABPA/B in high grade gliomas
Abstract
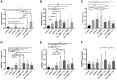
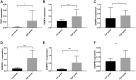
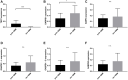
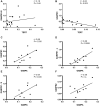
Enhanced expression of TERT in gliomas is a result of two hotspot mutations, C228T and C250T, at the promoter region. GA-binding proteins selectively bind at these positions, respectively, causing an activation of the promoter and overexpression of TERT. GABP is a multimeric protein consisting of GABPA and GABPB with its isoforms GABPB1, GABPB1-L, GABPB1-S, GABPB2. In this study, we investigated the mRNA expression and association between TERT and GABPA/B isoforms in tumor samples of different glioma grades. The expression was determined by quantitative real-time PCR and the results were statistically analyzed. We present that TERT is mainly expressed in primary glioblastomas. All GA-binding proteins progress through the glioma grades and have the highest expression levels in secondary glioblastomas. In secondary glioblastomas after chemotherapy, GABPB1 and GABPB1-L are expressed on a lower level than without treatment. In high grades, TERT and GABPA, GAPB1, GABPB1-L, GABPB1-S are upregulated compared to low grades. Between primary and secondary glioblastomas with and without chemotherapy, TERT is elevated in the former while GABPB1 is increased in the secondary glioblastomas. GABPA and GABPB1, GABPB1-L and GABPB1-S positive correlate in primary glioblastomas. The present study confirms the upregulation of TERT in primary glioblastomas while all GABP proteins rise with the malignancy of the gliomas. Further investigations must be made to elucidate the relation between TERT and all GABP proteins as it may play a key role in the gliomagenesis.
Keywords: GABPA; GABPB; TERT; astrocytoma; glioma.
Copyright: © 2021 Papazacharias et al.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare that the article content was composed in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TERT promoter mutations and GABP transcription factors in carcinogenesis: More foes than friends.Cancer Lett. 2020 Nov 28;493:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.07.003. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Cancer Lett. 2020. PMID: 32768523 Review.
-
Downregulation and Hypermethylation of GABPB1 Is Associated with Aggressive Thyroid Cancer Features.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 8;14(6):1385. doi: 10.3390/cancers14061385. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35326537 Free PMC article.
-
GABPA is a master regulator of luminal identity and restrains aggressive diseases in bladder cancer.Cell Death Differ. 2020 Jun;27(6):1862-1877. doi: 10.1038/s41418-019-0466-7. Epub 2019 Dec 4. Cell Death Differ. 2020. PMID: 31802036 Free PMC article.
-
TERT promoter mutations in primary and secondary glioblastomas.Acta Neuropathol. 2013 Dec;126(6):931-7. doi: 10.1007/s00401-013-1163-0. Epub 2013 Aug 17. Acta Neuropathol. 2013. PMID: 23955565
-
TERT promoter mutation and its interaction with IDH mutations in glioma: Combined TERT promoter and IDH mutations stratifies lower-grade glioma into distinct survival subgroups-A meta-analysis of aggregate data.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2017 Dec;120:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2017.09.013. Epub 2017 Oct 3. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2017. PMID: 29198322 Review.
References
-
- Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Kleihues P, Ellison DW. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016; 131:803–20. 10.1007/s00401-016-1545-1. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

