Spectrum of Drug Resistance in Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis
- PMID: 34194646
- PMCID: PMC8192612
- DOI: 10.1007/s43465-021-00378-6
Spectrum of Drug Resistance in Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis
Abstract
Background: Very few studies report resistance pattern exclusively in musculoskeletal tuberculosis (MSK-TB).
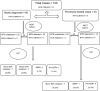
Methods: This study of 100 pus samples from patients of MSK-TB with active disease in whom Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) was detected by cartridge-based nucleic acid amplification test (CBNAAT), revealed the pattern of resistance among newly diagnosed and previously treated cases. Liquid culture and drug susceptibility testing (DST) using MGIT 960 was done for 11 anti-tubercular drugs.
Results: Among these 100 cases; 22% were AFB positive; MGIT 960 detected MTB in 58.33% (35/60) new cases and 30.0% (12/40) previously treated cases. Five new and 10 previously treated cases had drug resistance and 12 were detected rifampicin resistance (Rif-R) by CBNAAT. Among new cases MGIT-DST detected mono-INH resistant in 2.86% (1/35), mono-STR resistant in 2.86% (1/35), MDR-TB in 5.7% (2/35) and pre-XDR in 2.9%(1/35).Among previously treated cases Rif-R was found in 10% (4/40) where MTB was not detected by MGIT and MGIT-DST detected mono-INH resistant in 8.33% (1/12); MDR-TB in 8.33% (1/12) and pre-XDR in 33.3%. There were no cases of XDR-TB.
Conclusion: High disease burden of various type drug resistance were seen more commonly in previously treated cases and was not uncommon in new cases of MSK-TB. Both CBNAAT and DST are essential for detecting resistance pattern in MSK-TB.
Keywords: Drug-resistant tuberculosis; EPTB; GeneXpert MTB/RIF; MSK-TB; Pre-XDR.
© Indian Orthopaedics Association 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Global tuberculosis report (2018). World Health Organization website. http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en. Accessed October 2019
-
- Tuli SM. Tuberculosis of the skeletal system (bones, joints, spine and bursal sheaths) 3. New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers Press; 2004.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources