Dabigatran mitigates cisplatin-mediated nephrotoxicity through down regulation of thrombin pathway
- PMID: 34194837
- PMCID: PMC8240102
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2020.12.014
Dabigatran mitigates cisplatin-mediated nephrotoxicity through down regulation of thrombin pathway
Abstract
Introduction: Cisplatin (CDDP) nephrotoxicity is one of the most significant complications limiting its use in cancer therapy.
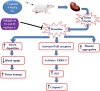
Objectives: This study investigated the pivotal role played by thrombin in CDDP-mediated nephrotoxicity. This work also aimed to clarify the possible preventive effect of Dabigatran (Dab), a direct thrombin inhibitor, on CDDP nephrotoxicity.
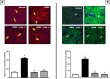
Methods: Animals were grouped as follow; normal control group, CDDP nephrotoxicity group, CDDP + Dab 15, and CDDP + Dab 25 groups. Four days following CDDP administration, blood and urine samples were collected to evaluate renal function. Moreover, tissue samples were collected from the kidney to determine apoptosis markers, oxidative stress and histopathological evaluation. An immunofluorescence analysis of tissue factor (TF), thrombin, protease-activated receptor-2 (PAR2), fibrin, pERK1/2 and P53 proteins expression was also performed.
Results: Thrombin, pERK, cleaved caspase-3, and oxidative stress markers were significantly elevated in CDDP-treated group. However, pretreatment of animals with either low or high doses of Dab significantly improved kidney function and decreased oxidative stress and apoptotic markers.
Conclusion: We conclude that thrombin is an important factor in the pathogenesis of CDDP kidney toxicity via activation of ERK1/2, P53 and caspase-3 pathway, which can be effectively blocked by Dab.
Keywords: BUN, Blood urea nitrogen; CDDP, Cisplatin; Cisplatin; Cr, creatinine; Crcl, Creatinine clerance; Dab, Dabigatran; Dabigatran; FXa, activated form of Factor X; GSH, Reduced Glutathion; H&E, Hematoxylin–Eosin; INR, International normalized ratio; KIM-1, kidney injury molecule-1; PAR, protease-activated receptor; PAR2; Pt, Prothrombin time; Ptt, Partial thromboplastin time; ROS, Reactive oxygen species; SOD, Superoxide dismutase; TF, Tissue factor; Thrombin; pERK1/2.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Cairo University.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Türk G., Ateşşahin A., Sönmez M., Çeribaşi A.O., Yüce A. Improvement of cisplatin-induced injuries to sperm quality, the oxidant-antioxidant system, and the histologic structure of the rat testis by ellagic acid. Fertil Steril. 2008;89:1474–1481. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2007.04.059. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

