Purification of high molecular weight thermotolerant esterase from Serratia sp. and its characterization
- PMID: 34194900
- PMCID: PMC8172709
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-021-02852-2
Purification of high molecular weight thermotolerant esterase from Serratia sp. and its characterization
Abstract
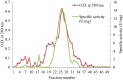
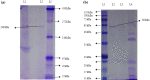
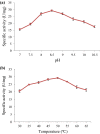
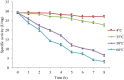
In the present study, an extracellular esterase from Serratia sp. was purified 24.46 fold using an initial ammonium sulphate precipitation step (optimized concentration of 30-40%), followed by Diethylaminoethyl cellulose (DEAE-cellulose) chromatography and size exclusion Sephadex G-200 column chromatography steps. The molecular weight of the esterase using native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) was determined to be 236 kDa and by using sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) was found to be 60 kDa suggesting that the enzyme was a tetramer of 4 subunits. The purified esterase was able to catalyze the hydrolysis of p-nitrophenyl esters, especially p-nitrophenyl acetate. Maximum esterase activity was achieved in 0.15 M Tris-HCl buffer of pH 8.5 at 50 °C after 10 min. The enzyme was stable for at least 8 h at 4 and 35 °C but the half-life was determined to be 4.5 h at 50 °C and 3 h at 60 °C. The esterase activity was inhibited by detergents (1 mM) (Triton X-100, Tween 60, Tween 80, ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid and SDS) except Tween 20. The esterase activity was inhibited by organic solvents (1 mM) such as ethanol, methanol, acetone, acetonitrile and was stable in the presence of glycerol, isopropanol but the organic solvent dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) significantly (p < 0.05) enhanced esterase activity. The matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry showed that the enzyme exhibited similarity with the pimeloyl-[acyl carrier protein] methyl ester esterase of Serratia marcescens.
Keywords: Diethylaminoethyl cellulose; Esterase; Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry; SDS-PAGE; Tris–HCl buffer; p-NPA.
© King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Ayna C, Kolcuoğlu Y, Öz F, Colak A, Ertunga NS. Purification and characterization of a pH and heat stable esterase from Geobacillus sp. TF17. Turk J Biochem. 2013;38:329–336. doi: 10.5505/tjb.2013.36035. - DOI
-
- Bisswanger H. Enzyme assays. Perspect Sci. 2014;1:41–55. doi: 10.1016/j.pisc.2014.02.005. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

