Topological Encoded Vector Beams for Monitoring Amyloid-Lipid Interactions in Microcavity
- PMID: 34194941
- PMCID: PMC8224421
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202100096
Topological Encoded Vector Beams for Monitoring Amyloid-Lipid Interactions in Microcavity
Abstract
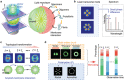
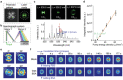
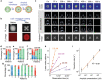
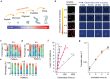
Lasers are the pillars of modern photonics and sensing. Recent advances in microlasers have demonstrated its extraordinary lasing characteristics suitable for biosensing. However, most lasers utilized lasing spectrum as a detection signal, which can hardly detect or characterize nanoscale structural changes in microcavity. Here the concept of amplified structured light-molecule interactions is introduced to monitor tiny bio-structural changes in a microcavity. Biomimetic liquid crystal droplets with self-assembled lipid monolayers are sandwiched in a Fabry-Pérot cavity, where subtle protein-lipid membrane interactions trigger the topological transformation of output vector beams. By exploiting Amyloid β (Aβ)-lipid membrane interactions as a proof-of-concept, it is demonstrated that vector laser beams can be viewed as a topology of complex laser modes and polarization states. The concept of topological-encoded laser barcodes is therefore developed to reveal dynamic changes of laser modes and Aβ-lipid interactions with different Aβ assembly structures. The findings demonstrate that the topology of vector beams represents significant features of intracavity nano-structural dynamics resulted from structured light-molecule interactions.
Keywords: amyloid‐lipid interaction; laser modes; liquid crystals; microcavity; topological structures; vector beams.
© 2021 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Armani D. K., Kippenberg T. J., Spillane S. M., Vahala K. J., Nature 2003, 421, 925. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X., Cao Q. T., Wang Z., Liu Y. X., Qiu C. W., Yang L., Gong Q., Xiao Y. F., Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 21.
-
- Armani A. M., Kulkarni R. P., Fraser S. E., Flagan R. C., Vahala K. J., Science 2007, 317, 783. - PubMed
-
- Baaske M. D., Foreman M. R., Vollmer F., Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 933. - PubMed
-
- Chen W., Özdemir Ş. K., Zhao G., Wiersig J., Yang L., Nature 2017, 548, 192. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
