Cellular Contractility Profiles of Human Diabetic Corneal Stromal Cells
- PMID: 34194958
- PMCID: PMC8203386
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/9913210
Cellular Contractility Profiles of Human Diabetic Corneal Stromal Cells
Abstract
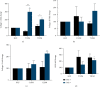
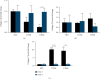
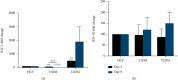
Diabetic keratopathy is a corneal complication of diabetes mellitus (DM). Patients with diabetic keratopathy are prone to developing corneal haze, scarring, recurrent erosions, and significant wound healing defects/delays. The purpose of this study was to determine the contractility profiles in the diabetic human corneal stromal cells and characterize their molecular signatures. Primary human corneal fibroblasts from healthy, Type 1 DM (T1DM), and Type 2 DM (T2DM) donors were cultured using an established 3D collagen gel model. We tracked, measured, and quantified the contractile footprint over 9 days and quantified the modulation of specific corneal/diabetes markers in the conditional media and cell lysates using western blot analysis. Human corneal fibroblasts (HCFs) exhibited delayed and decreased contractility compared to that from T1DMs and T2DMs. Compared to HCFs, T2DMs demonstrated an initial downregulation of collagen I (day 3), followed by a significant upregulation by day 9. Collagen V was significantly upregulated in both T1DMs and T2DMs based on basal secretion, when compared to HCFs. Cell lysates were upregulated in the myofibroblast-associated marker, α-smooth muscle actin, in T2DMs on day 9, corresponding to the significant increase in contractility rate observed at the same time point. Furthermore, our data demonstrated a significant upregulation in IGF-1 expression in T2DMs, when compared to HCFs and T1DMs, at day 9. T1DMs demonstrated significant downregulation of IGF-1 expression, when compared to HCFs. Overall, both T1DMs and T2DMs exhibited increased contractility associated with fibrotic phenotypes. These findings, and future studies, may contribute to better understanding of the pathobiology of diabetic keratopathy and ultimately the development of new therapeutic approaches.
Copyright © 2021 Thi N. Lam et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The corresponding author is the chief editor of ACP. All other authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Unravelling the stromal-nerve interactions in the human diabetic cornea.Exp Eye Res. 2017 Nov;164:22-30. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2017.08.003. Epub 2017 Aug 5. Exp Eye Res. 2017. PMID: 28827027 Free PMC article.
-
Nerve influence on the metabolism of type I and type II diabetic corneal stroma: an in vitro study.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 1;11(1):13627. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-93164-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34211074 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of hypoxia in the diabetic corneal stroma microenvironment.Exp Eye Res. 2024 Mar;240:109790. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2024.109790. Epub 2024 Jan 14. Exp Eye Res. 2024. PMID: 38224848
-
[The cornea: stasis and dynamics].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2008 Mar;112(3):179-212; discussion 213. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2008. PMID: 18411711 Review. Japanese.
-
Corneal changes in diabetes mellitus.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2012 Jul 1;8(4):294-302. doi: 10.2174/157339912800840479. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2012. PMID: 22587515 Review.
Cited by
-
Unravelling Novel Roles of Salivary Exosomes in the Regulation of Human Corneal Stromal Cell Migration and Wound Healing.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 14;23(8):4330. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084330. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457149 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of sensory neuropathy and inflammation on epithelial wound healing in diabetic corneas.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2022 Jul;89:101039. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2021.101039. Epub 2022 Jan 4. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2022. PMID: 34991965 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Danaei G., Finucane M. M., Lu Y., et al. National, regional, and global trends in fasting plasma glucose and diabetes prevalence since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 370 country-years and 27 million participants. Lancet. 2011;378(9785):31–40. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(11)60679-x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

