Molecular dynamics, quantum mechanics and docking studies of some Keap1 inhibitors - An insight into the atomistic mechanisms of their antioxidant potential
- PMID: 34195424
- PMCID: PMC8233138
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07317
Molecular dynamics, quantum mechanics and docking studies of some Keap1 inhibitors - An insight into the atomistic mechanisms of their antioxidant potential
Abstract
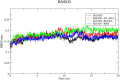
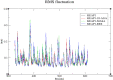
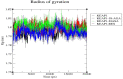
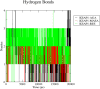
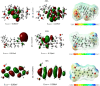
Inhibitors of Keap1 would disrupt the covalent interaction between Keap1 and Nrf2 to unleash Nrf2 transcriptional machinery that orchestrates its cellular antioxidant, cytoprotective and detoxification processes thereby, protecting the cells against oxidative stress mediated diseases. In this in silico research, we investigated the Keap1 inhibiting potential of fifty (50) antioxidants using pharmacokinetic ADMET profiling, bioactivity assessment, physicochemical studies, molecular docking investigation, molecular dynamics and Quantum mechanical-based Density Functional Theory (DFT) studies using Keap1 as the apoprotein control. Out of these 50 antioxidants, Maslinic acid (MASA), 18-alpha-glycyrrhetinic acid (18-AGA) and resveratrol stand out by passing the RO5 (Lipinski rule of 5) for the physicochemical properties and ADMET studies. These three compounds also show high binding affinity of -10.6 kJ/mol, -10.4 kJ/mol and -7.8 kJ/mol at the kelch pocket of Keap1 respectively. Analysis of the 20ns trajectories using RMSD, RMSF, ROG and h-bond parameters revealed the stability of these compounds after comparing them with Keap1 apoprotein. Furthermore, the electron donating and accepting potentials of these compounds was used to investigate their reactivity using Density Functional Theory (HOMO and LUMO) and it was revealed that resveratrol had the highest stability based on its low energy gap. Our results predict that the three compounds are potential drug candidates with domiciled therapeutic functions against oxidative stress-mediated diseases. However, resveratrol stands out as the compound with the best stability and therefore, could be the best candidate with the best therapeutic efficacy.
Keywords: Density functional theory; Keap1; Molecular docking; Molecular dynamics.
© 2021 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exploring the inhibitory potentials of Momordica charantia bioactive compounds against Keap1-Kelch protein using computational approaches.In Silico Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 25;9(1):39. doi: 10.1007/s40203-021-00100-2. eCollection 2021. In Silico Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34249600 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the New Inhibitors by Sulfadiazine and Modified Derivatives of α-D-glucopyranoside for White Spot Syndrome Virus Disease of Shrimp by In Silico: Quantum Calculations, Molecular Docking, ADMET and Molecular Dynamics Study.Molecules. 2022 Jun 8;27(12):3694. doi: 10.3390/molecules27123694. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35744817 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of NRF2/KEAP1-Mediated Oxidative Stress for Cancer Treatment by Natural Products Using Pharmacophore-Based Screening, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Studies.Molecules. 2023 Aug 10;28(16):6003. doi: 10.3390/molecules28166003. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37630254 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (NRF2) drug discovery: Biochemical toolbox to develop NRF2 activators by reversible binding of Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1).Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017 Oct 1;631:31-41. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2017.08.003. Epub 2017 Aug 8. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2017. PMID: 28801166 Review.
-
Discovery of direct inhibitors of Keap1-Nrf2 protein-protein interaction as potential therapeutic and preventive agents.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015 Jul;5(4):285-99. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2015.05.008. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015. PMID: 26579458 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Study on the molecular mechanism of anti-liver cancer effect of Evodiae fructus by network pharmacology and QSAR model.Front Chem. 2023 Jan 9;10:1060500. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.1060500. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 36700075 Free PMC article.
-
Tapping into Nature's Arsenal: Harnessing the Potential of Natural Antioxidants for Human Health and Disease Prevention.Foods. 2024 Jun 25;13(13):1999. doi: 10.3390/foods13131999. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38998505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Antioxidant Peptides from Grateloupia livida Hydrolysates: Purification and Identification.Foods. 2022 May 20;11(10):1498. doi: 10.3390/foods11101498. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35627068 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulation revealed promising drug candidates of p53-MDM2 interaction.J Mol Model. 2022 May 10;28(6):142. doi: 10.1007/s00894-022-05131-w. J Mol Model. 2022. PMID: 35536362
-
Echinochrome Ameliorates Physiological, Immunological, and Histopathological Alterations Induced by Ovalbumin in Asthmatic Mice by Modulating the Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway.Mar Drugs. 2023 Aug 18;21(8):455. doi: 10.3390/md21080455. Mar Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37623736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Bont R., van Larebeke N. Endogenous DNA damage in humans: a review of quantitative data. Mutagenesis. 2004 May;19(3):169–185. - PubMed
-
- Dinkova-Kostova A.T., Talalay P. Direct and indirect antioxidant properties of inducers of cytoprotective proteins. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008 Jun;52(Suppl 1):S128–S138. PMID: 18327872. - PubMed
-
- Lu M.C., Ji J.A., Jiang Z.Y., You Q.D. The keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway as a potential preventive and therapeutic target: an update. Med. Res. Rev. 2016 Sep;36(5):924–963. 2016 May 18. PMID: 27192495. - PubMed
-
- Keleku-Lukwete N., Suzuki M., Yamamoto M. An overview of the advantages of KEAP1-NRF2 system Activation during inflammatory disease treatment. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2018;29(17):1746–1755. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

