Baricitinib and primary biliary cholangitis
- PMID: 34195587
- PMCID: PMC8240017
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2021.100107
Baricitinib and primary biliary cholangitis
Abstract
Background and aims: There is an unmet need for alternative treatments for patients with primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) who do not respond to treatment with ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA). A proof-of-concept study of baricitinib, an orally administered Janus kinase 1 and 2 inhibitor, was initiated to evaluate its use in PBC patients.
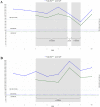
Approach and results: Patients with PBC showing inadequate response or intolerance to UDCA were eligible. This was a randomized, double-blinded placebo-controlled trial. Enrollees were assigned 1:1 to baricitinib (2 mg/day) or placebo. Endpoints included change in alkaline phosphatase (ALP), itch Numeric Rating Score (NRS), and fatigue NRS at 12 weeks post-baseline; exploratory markers included high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and Enhanced Liver Fibrosis (ELF) score.Due to low enrollment, the study was terminated early. Two patients were enrolled and completed the trial; 1 was randomized to receive baricitinib and 1 to placebo. Over the treatment period, the baricitinib-treated patient demonstrated a 30% decrease in ALP and a 7-point improvement in the itch NRS, but a 2-point increase in the Fatigue NRS. Markers of inflammation and liver fibrosis (hs-CRP and ELF score) also improved over the study period. In contrast, the placebo-treated patient showed no improvement in primary or secondary endpoints. A single non-serious treatment-emergent adverse event of moderate sinusitis was reported by the baricitinib-treated patient at day 47.
Conclusions: In a 12-week trial, a patient with PBC showing inadequate response to treatment with UDCA demonstrated a dramatic response to treatment with baricitinib.
Keywords: 12-Week; Itch; Jak1/2 inhibitors; Liver disease.
© 2021 The Authors.
Figures
References
-
- Kaplan M.M., Gershwin M.E. Primary biliary cirrhosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005;353:1261–1273. - PubMed
-
- Lindor K.D., Gershwin M.E., Poupon R., Kaplan M., Bergasa N.V., Heathcote E.J. Primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2009;50:291–308. - PubMed
-
- Kuiper E.M.M., Hansen B.E., de Vries R.A., den Ouden-Muller J.W., can Ditzhuijsen Tjm, Haagsma E.B. Improved prognosis of patients with primary biliary cirrhosis that have a biochemical response to ursodeoxycholic acid. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:1281–1287. - PubMed
-
- Pares A., Caballeria L., Rodes J. Excellent long‐term survival in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis and biochemical response to ursodeoxycholic Acid. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:715–720. - PubMed
-
- Corpechot C., Abenavoli L., Rabahi N., Chrétien Y., Andréani T., Johanet C. Biochemical response to ursodeoxycholic acid and long‐term prognosis in primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2008;48:871–877. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

