Targeting Canonical and Non-Canonical STAT Signaling Pathways in Renal Diseases
- PMID: 34199002
- PMCID: PMC8305338
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10071610
Targeting Canonical and Non-Canonical STAT Signaling Pathways in Renal Diseases
Abstract
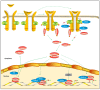
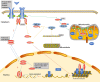
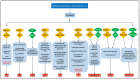
Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) plays an essential role in the inflammatory reaction and immune response of numerous renal diseases. STATs can transmit the signals of cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors from the cell membrane to the nucleus. In the canonical STAT signaling pathways, upon binding with their cognate receptors, cytokines lead to a caspase of Janus kinases (JAKs) and STATs tyrosine phosphorylation and activation. Besides receptor-associated tyrosine kinases JAKs, receptors with intrinsic tyrosine kinase activities, G-protein coupled receptors, and non-receptor tyrosine kinases can also activate STATs through tyrosine phosphorylation or, alternatively, other post-translational modifications. Activated STATs translocate into the nucleus and mediate the transcription of specific genes, thus mediating the progression of various renal diseases. Non-canonical STAT pathways consist of preassembled receptor complexes, preformed STAT dimers, unphosphorylated STATs (U-STATs), and non-canonical functions including mitochondria modulation, microtubule regulation and heterochromatin stabilization. Most studies targeting STAT signaling pathways have focused on canonical pathways, but research extending into non-canonical STAT pathways would provide novel strategies for treating renal diseases. In this review, we will introduce both canonical and non-canonical STAT pathways and their roles in a variety of renal diseases.
Keywords: STAT; renal diseases; signal transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mudter J., Weigmann B., Bartsch B., Kiesslich R., Strand D., Galle P.R., Lehr H.A., Schmidt J., Neurath M.F. Activation pattern of signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) factors in inflammatory bowel diseases. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005;100:64–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2005.40615.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

