Estimation of Respiratory Rate from Thermography Using Respiratory Likelihood Index
- PMID: 34199084
- PMCID: PMC8271612
- DOI: 10.3390/s21134406
Estimation of Respiratory Rate from Thermography Using Respiratory Likelihood Index
Abstract
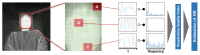
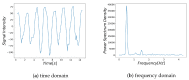
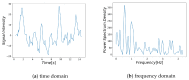
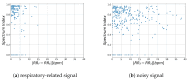
Respiration is a key vital sign used to monitor human health status. Monitoring respiratory rate (RR) under non-contact is particularly important for providing appropriate pre-hospital care in emergencies. We propose an RR estimation system using thermal imaging cameras, which are increasingly being used in the medical field, such as recently during the COVID-19 pandemic. By measuring temperature changes during exhalation and inhalation, we aim to track the respiration of the subject in a supine or seated position in real-time without any physical contact. The proposed method automatically selects the respiration-related regions from the detected facial regions and estimates the respiration rate. Most existing methods rely on signals from nostrils and require close-up or high-resolution images, while our method only requires the facial region to be captured. Facial region is detected using YOLO v3, an object detection model based on deep learning. The detected facial region is divided into subregions. By calculating the respiratory likelihood of each segmented region using the newly proposed index, called the Respiratory Quality Index, the respiratory region is automatically selected and the RR is estimated. An evaluation of the proposed RR estimation method was conducted on seven subjects in their early twenties, with four 15 s measurements being taken. The results showed a mean absolute error of 0.66 bpm. The proposed method can be useful as an RR estimation method.
Keywords: deep learning; likelihood index; object detection; signal processing; thermal imaging; vital sign measurement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Braun S.K. RR and pattern. In: Walker H.K., Hall W.D., Hurst J.W., editors. Clinical Methods: The History, Physical, and Laboratory Examinations. 3rd ed. Butterworths; Atlanta, GA, USA: 1990. pp. 226–230. - PubMed
-
- Tong H. In: Nonlinear Time Series: A Dynamical System Approach. Elsner J.B., editor. Oxford University Press; Oxford, UK: 1990.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

