The Crossroads between Zinc and Steroidal Implant-Induced Growth of Beef Cattle
- PMID: 34199133
- PMCID: PMC8300159
- DOI: 10.3390/ani11071914
The Crossroads between Zinc and Steroidal Implant-Induced Growth of Beef Cattle
Abstract
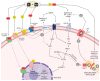
Growth-promoting technologies such as steroidal implants have been utilized in the beef industry for over 60 years and remain an indispensable tool for improving economic returns through consistently improved average daily gain via increased skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Zinc has been implicated in skeletal muscle growth through protein synthesis, satellite cell function, and many other growth processes. Therefore, the objective of this review was to present the available literature linking Zn to steroidal implant-induced protein synthesis and other metabolic processes. Herein, steroidal implants and their mode of action, the biological importance of Zn, and several connections between steroidal implants and Zn related to growth processes are discussed. These include the influence of Zn on hormone receptor signaling, circulating insulin-like growth factor-1 concentrations, glucose metabolism, protein synthesis via mTOR, and satellite cell proliferation and differentiation. Supplemental Zn has also been implicated in improved growth rates of cattle utilizing growth-promoting technologies, and steroidal implants appear to alter liver and circulating Zn concentrations. Therefore, this review provides evidence of the role of Zn in steroidal implant-induced growth yet reveals gaps in the current knowledge base related to optimizing Zn supplementation strategies to best capture growth performance improvements offered through steroidal implants.
Keywords: cattle; estradiol; growth; hormones; trace minerals; trenbolone acetate; zinc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of increasing supplemental zinc in beef feedlot steers administered a steroidal implant and beta agonist.Transl Anim Sci. 2022 Feb 28;6(2):txac029. doi: 10.1093/tas/txac029. eCollection 2022 Apr. Transl Anim Sci. 2022. PMID: 35382158 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc supplementation strategies in feedlot heifers receiving an extended-release implant or an aggressive re-implant program.J Anim Sci. 2021 Aug 1;99(8):skab212. doi: 10.1093/jas/skab212. J Anim Sci. 2021. PMID: 34261132 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of flax supplementation and a combined trenbolone acetate and estradiol implant on circulating insulin-like growth factor-I and muscle insulin-like growth factor-I messenger RNA levels in beef cattle.J Anim Sci. 2003 Dec;81(12):3028-34. doi: 10.2527/2003.81123028x. J Anim Sci. 2003. PMID: 14677858
-
MEAT SCIENCE AND MUSCLE BIOLOGY SYMPOSIUM--role of satellite cells in anabolic steroid-induced muscle growth in feedlot steers.J Anim Sci. 2014 Jan;92(1):30-8. doi: 10.2527/jas.2013-7077. Epub 2013 Oct 28. J Anim Sci. 2014. PMID: 24166993 Review.
-
Application of cellular mechanisms to growth and development of food producing animals.J Anim Sci. 2008 Apr;86(14 Suppl):E226-35. doi: 10.2527/jas.2007-0450. Epub 2007 Oct 26. J Anim Sci. 2008. Retraction in: J Anim Sci. 2008 Jul;86(7):1724. doi: 10.2527/jas.2008-86-7-1724. PMID: 17965330 Retracted. Review.
Cited by
-
Current Research, Industrialization Status, and Future Perspective of Cultured Meat.Food Sci Anim Resour. 2024 Mar;44(2):326-355. doi: 10.5851/kosfa.2024.e13. Epub 2024 Mar 1. Food Sci Anim Resour. 2024. PMID: 38764517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NC1184: Molecular Mechanisms Regulating Skeletal Muscle Growth and Differentiation.J Anim Sci. 2022 Aug 1;100(8):skac229. doi: 10.1093/jas/skac229. J Anim Sci. 2022. PMID: 35908784 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Mineral composition of serially slaughtered Holstein steers supplemented with zilpaterol hydrochloride.J Anim Sci. 2023 Jan 3;101:skad209. doi: 10.1093/jas/skad209. J Anim Sci. 2023. PMID: 37343300 Free PMC article.
-
Trace Mineral Nutrition of Grazing Beef Cattle.Animals (Basel). 2021 Sep 22;11(10):2767. doi: 10.3390/ani11102767. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34679788 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Genther-Schroeder O.N., Branine M.E., Hansen S.L. The effects of increasing supplementation of zinc-amino acid complex on growth performance, carcass characteristics, and inflammatory response of beef cattle fed ractopamine hydrochloride. J. Anim. Sci. 2016;94:3389–3398. doi: 10.2527/jas.2015-0209. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

