Bioimpedance Vector Patterns according to Age and Handgrip Strength in Adolescent Male and Female Athletes
- PMID: 34199903
- PMCID: PMC8200122
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18116069
Bioimpedance Vector Patterns according to Age and Handgrip Strength in Adolescent Male and Female Athletes
Abstract
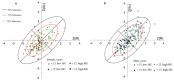
Bioelectric Impedance Vector Analysis (BIVA) can be used to qualitatively compare individuals' hydration and cell mass independently of predictive equations. This study aimed to analyze the efficiency of BIVA considering chronological age and handgrip strength in adolescent athletes. A total of 273 adolescents (male; 59%) engaged in different sports were evaluated. Bioelectrical impedance (Z), resistance (R), reactance (Xc), and phase angle (PhA) were obtained using a single-frequency bioelectrical impedance analyzer. Fat-free mass (FFM) and total body water were estimated using bioimpedance-based equations specific for adolescents. Female showed higher values of R (5.5%, p = 0.001), R/height (3.8%, p = 0.041), Z (5.3%, p = 0.001), and fat mass (53.9%, p = 0.001) than male adolescents. Male adolescents showed higher values of FFM (5.3%, p = 0.021) and PhA (3.1%, p = 0.033) than female adolescents. In both stratifications, adolescents (older > 13 years or stronger > median value) shifted to the left on the R-Xc graph, showing patterns of higher hydration and cell mass. The discrimination of subjects older than 13 years and having higher median of handgrip strength values was possibly due to maturity differences. This study showed that BIVA identified age and strength influence in vector displacement, assessing qualitative information and offering patterns of vector distribution in adolescent athletes.
Keywords: BIVA; R-Xc graph; adolescent athletes; body composition; confidence ellipses; fat-free mass; tolerance ellipses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
One-Year Changes in Bioelectrical Impedance Data in Adolescent Athletes.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 29;16(5):701. doi: 10.3390/nu16050701. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38474828 Free PMC article.
-
Classic Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Reference Values for Assessing Body Composition in Male and Female Athletes.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Dec 12;16(24):5066. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16245066. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31842289 Free PMC article.
-
Phase angle and bioelectrical impedance vector analysis in the evaluation of body composition in athletes.Clin Nutr. 2020 Feb;39(2):447-454. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2019.02.016. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Clin Nutr. 2020. PMID: 30850270
-
Bioelectrical impedance analysis versus reference methods in the assessment of body composition in athletes.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2022 Mar;122(3):561-589. doi: 10.1007/s00421-021-04879-y. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35067750
-
Assessment of Body Composition in Athletes: A Narrative Review of Available Methods with Special Reference to Quantitative and Qualitative Bioimpedance Analysis.Nutrients. 2021 May 12;13(5):1620. doi: 10.3390/nu13051620. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34065984 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
One-Year Changes in Bioelectrical Impedance Data in Adolescent Athletes.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 29;16(5):701. doi: 10.3390/nu16050701. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38474828 Free PMC article.
-
Growth, Somatic Maturation, and Their Impact on Physical Health and Sports Performance: An Editorial.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jan 24;19(3):1266. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19031266. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35162287 Free PMC article.
-
The science of bioelectrical impedance-derived phase angle: insights from body composition in youth.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2025 Aug;26(4):603-624. doi: 10.1007/s11154-025-09964-7. Epub 2025 Apr 10. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2025. PMID: 40208410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Age-, sex-, and maturity-associated variation in the phase angle after adjusting for size in adolescents.Front Nutr. 2022 Aug 1;9:939714. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.939714. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35978953 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between Bioelectrical Impedance Phase Angle and Upper and Lower Limb Muscle Strength in Athletes from Several Sports: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis.Sports (Basel). 2023 May 18;11(5):107. doi: 10.3390/sports11050107. Sports (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37234063 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bielemann R.M., Domingues M.R., Horta B.L., Menezes A.M.B., Gonçalves H., Assunção M.C.F., Hallal P.C. Physical activity throughout adolescence and bone mineral density in early adulthood: The 1993 Pelotas (Brazil) Birth Cohort Study. Osteoporos. Int. 2014;25:2007–2015. doi: 10.1007/s00198-014-2715-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jiménez-Pavón D., Fernández-Vázquez A., Alexy U., Pedrero R., Cuenca-García M., Polito A., Vanhelst J., Manios Y., Kafatos A., Molnar D., et al. Association of objectively measured physical activity with body components in European adolescents. BMC Public Health. 2013;13:667–675. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-13-667. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moliner-Urdiales D., Ortega F.B., Vicente-Rodriguez G., Rey-Lopez J.P., Gracia-Marco L., Widhalm K., Sjöström M., Moreno L.A., Castillo M.J., Ruiz J.R. Association of physical activity with muscular strength and fat-free mass in adolescents: The HELENA study. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010;109:1119–1127. doi: 10.1007/s00421-010-1457-z. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

