Expression of X-Linked Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein (XIAP) in Breast Cancer Is Associated with Shorter Survival and Resistance to Chemotherapy
- PMID: 34199946
- PMCID: PMC8200223
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13112807
Expression of X-Linked Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein (XIAP) in Breast Cancer Is Associated with Shorter Survival and Resistance to Chemotherapy
Abstract
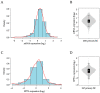
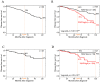
XIAP, the most potent inhibitor of cell death pathways, is linked to chemotherapy resistance and tumor aggressiveness. Currently, multiple XIAP-targeting agents are in clinical trials. However, the characterization of XIAP expression in relation to clinicopathological variables in large clinical series of breast cancer is lacking. We retrospectively analyzed non-metastatic, non-inflammatory, primary, invasive breast cancer samples for XIAP mRNA (n = 2341) and protein (n = 367) expression. XIAP expression was analyzed as a continuous value and correlated with clinicopathological variables. XIAP mRNA expression was heterogeneous across samples and significantly associated with younger patients' age (≤50 years), pathological ductal type, lower tumor grade, node-positive status, HR+/HER2- status, and PAM50 luminal B subtype. Higher XIAP expression was associated with shorter DFS in uni- and multivariate analyses in 909 informative patients. Very similar correlations were observed at the protein level. This prognostic impact was significant in the HR+/HER2- but not in the TN subtype. Finally, XIAP mRNA expression was associated with lower pCR rate to anthracycline-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy in both uni- and multivariate analyses in 1203 informative patients. Higher XIAP expression in invasive breast cancer is independently associated with poorer prognosis and resistance to chemotherapy, suggesting the potential therapeutic benefit of targeting XIAP.
Keywords: HER2; TN; XIAP; anthracycline; apoptosis; cell death; luminal B; metastasis; pCR; proteomics; taxanes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis positive nuclear labeling: a new independent prognostic biomarker of breast invasive ductal carcinoma.Diagn Pathol. 2011 Jun 7;6:49. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-6-49. Diagn Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21645409 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of resistance to systemic therapy in patients with breast cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;608:1-22. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-74039-3_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17993229 Review.
-
PAM50 Subtypes in Baseline and Residual Tumors Following Neoadjuvant Trastuzumab-Based Chemotherapy in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer: A Consecutive-Series From a Single Institution.Front Oncol. 2019 Aug 6;9:707. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00707. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31448227 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of predictive and prognostic value of androgen receptor expression in breast cancer subtypes treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy.Discov Oncol. 2023 Apr 26;14(1):49. doi: 10.1007/s12672-023-00660-z. Discov Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37099044 Free PMC article.
-
Ki67 and lymphocytes in the pretherapeutic core biopsy of primary invasive breast cancer: positive markers of therapy response prediction and superior survival.Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2017 Sep 22;32(2):/j/hmbci.2017.32.issue-2/hmbci-2017-0022/hmbci-2017-0022.xml. doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2017-0022. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2017. PMID: 28937963 Review.
Cited by
-
Editorial: Targeting different programmed cell death processes as therapeutic modalities for thyroid cancer.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jul 27;14:1255259. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1255259. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37576979 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Adaptive stress response genes associated with breast cancer subtypes and survival outcomes reveal race-related differences.NPJ Breast Cancer. 2022 Jun 13;8(1):73. doi: 10.1038/s41523-022-00431-z. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35697736 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of E3 ubiquitin ligases in cancer progression and targeted therapy.Clin Transl Med. 2023 Mar;13(3):e1204. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1204. Clin Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36881608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Jellyfish as an Alternative Source of Bioactive Antiproliferative Compounds.Mar Drugs. 2022 May 25;20(6):350. doi: 10.3390/md20060350. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35736153 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins to Overcome Chemotherapy Resistance-A Marriage between Targeted Therapy and Cytotoxic Chemotherapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 29;24(17):13385. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713385. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686191 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

