Paediatric Histoplasmosis 2000-2019: A Review of 83 Cases
- PMID: 34199970
- PMCID: PMC8229079
- DOI: 10.3390/jof7060448
Paediatric Histoplasmosis 2000-2019: A Review of 83 Cases
Abstract
Histoplasmosis is an endemic fungal infection that is confined to specific geographical regions. Histoplasma spp. are primary pathogens that cause disease in both immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients, ranging from a single-organ (mostly affecting the lungs) infection to life-threatening disseminated disease. Knowledge about the clinical epidemiology relies on data from adult populations; little is known about the patient and disease characteristics in the paediatric population. Therefore, a structured review of published cases of paediatric histoplasmosis between 2000 and 2019 was performed. A literature search of PubMed was conducted and the epidemiological and clinical data from 83 cases were analysed. The mean age at presentation was 9.5 ± 5.5 years, and 51% were girls. Two-thirds of the children were immunocompromised. The majority of children presented with disseminated disease. The most frequently observed clinical symptoms were respiratory symptoms, alongside non-specific systemic features, including fever, myalgia, fatigue and weight loss. The mortality rate was 11%. Histoplasmosis affects children of any age. Being immunocompromised is a risk factor for severe and disseminated disease. The lack of specific presenting features leads to underreporting and delay in diagnosis. To improve the recognition and outcome of histoplasmosis in childhood, increased awareness and surveillance systems are warranted.
Keywords: Histoplasma spp.; children; disseminated disease; histoplasmosis; infants; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
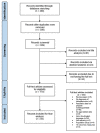
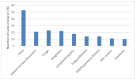
References
-
- Darling S. A protozoan general infection producing pseudo tubercles in the lungs and focal necroses in the liver, spleen and lymph nodes. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1906;46:1283–1285. doi: 10.1001/jama.1906.62510440037003. - DOI
-
- Dodd K., Tompkins E.H. A Case of Histoplasmosis of Darling in an Infant. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1934;14:127–137. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1934.s1-14.127. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

