PTD4 Peptide Increases Neural Viability in an In Vitro Model of Acute Ischemic Stroke
- PMID: 34200045
- PMCID: PMC8200211
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22116086
PTD4 Peptide Increases Neural Viability in an In Vitro Model of Acute Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
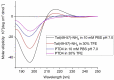
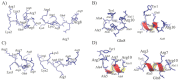
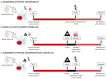
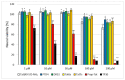
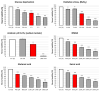
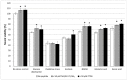
Ischemic stroke is a disturbance in cerebral blood flow caused by brain tissue ischemia and hypoxia. We optimized a multifactorial in vitro model of acute ischemic stroke using rat primary neural cultures. This model was exploited to investigate the pro-viable activity of cell-penetrating peptides: arginine-rich Tat(49-57)-NH2 (R49KKRRQRRR57-amide) and its less basic analogue, PTD4 (Y47ARAAARQARA57-amide). Our model included glucose deprivation, oxidative stress, lactic acidosis, and excitotoxicity. Neurotoxicity of these peptides was excluded below a concentration of 50 μm, and PTD4-induced pro-survival was more pronounced. Circular dichroism spectroscopy and molecular dynamics (MD) calculations proved potential contribution of the peptide conformational properties to neuroprotection: in MD, Tat(49-57)-NH2 adopted a random coil and polyproline type II helical structure, whereas PTD4 adopted a helical structure. In an aqueous environment, the peptides mostly adopted a random coil conformation (PTD4) or a polyproline type II helical (Tat(49-57)-NH2) structure. In 30% TFE, PTD4 showed a tendency to adopt a helical structure. Overall, the pro-viable activity of PTD4 was not correlated with the arginine content but rather with the peptide's ability to adopt a helical structure in the membrane-mimicking environment, which enhances its cell membrane permeability. PTD4 may act as a leader sequence in novel drugs for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke.
Keywords: PTD4; Tat(49–57)-NH2; arginine-rich peptides; cell-penetrating peptides; excitotoxicity; ischemic stroke; neural viability; neuroprotection; neurotoxicity; peptide conformation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Feigin V.L., Forouzanfar M.H., Krishnamurthi R., Mensah G.A., Connor M., Bennett D.A., Moran A.E., Sacco R.L., Anderson L., Truelsen T., et al. Global and regional burden of stroke during 1990–2010: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2014;383:245–254. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61953-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mozaffarian D., Benjamin E.J., Go A.S., Arnett D.K., Blaha M.J., Cushman M., Das S.R., de Ferranti S., Despres J.P., Fullerton H.J., et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2016 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;133:e38–e360. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000350. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Meloni B.P., Brookes L.M., Clark V.W., Cross J.L., Edwards A.B., Anderton R.S., Hopkins R.M., Hoffmann K., Knuckey N.W. Poly-arginine and arginine-rich peptides are neuroprotective in stroke models. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015;35:993–1004. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2015.11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

